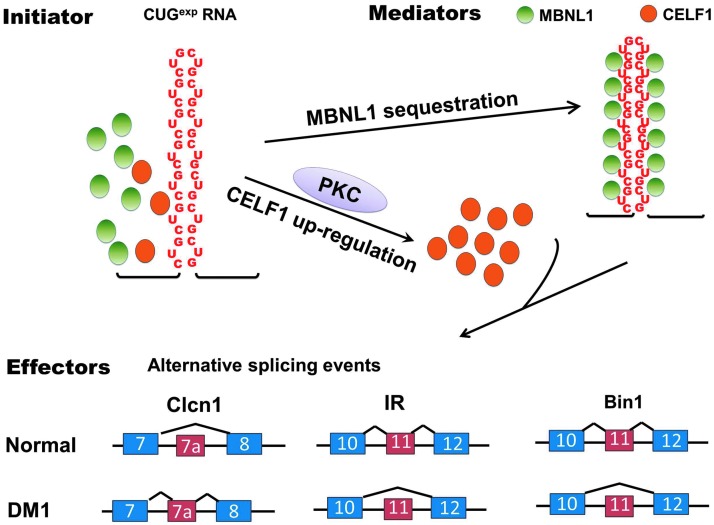
FIG. 1.
RNA-initiated toxicity in myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) pathogenesis. The expanded CUG repeats in the myotonic dystrophy protein kinase (dystrophia myotonica-protein kinase; DMPK) 3′ untranslated region (UTR) form a hairpin structure that binds to the splicing regulator muscleblind-like 1 (MBNL1) with high affinity, resulting in MBNL1 sequestration and loss-of-function. The CUG expansion (CUGexp) RNA also upregulates the levels of a second splicing factor, CUGBP Elav-like family member 1 (CELF1), by activation of protein kinase C (PKC). Disrupted function of MBNL1 and CELF1 leads to misregulation of a wide range of alternative splicing events including Clcn1, IR, and BIN1, directly contributing to clinical features of DM1.