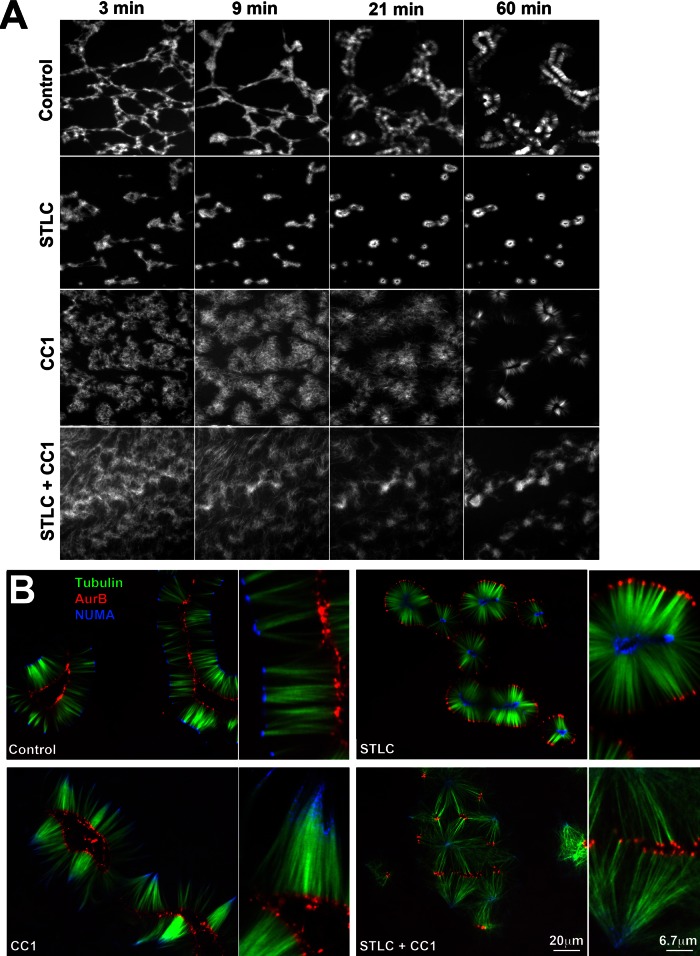
FIGURE 6:
Role of spindle assembly motors. (A) Time-course of assembly when kinesin-5 (Eg5), dynein or both motors were inhibited in parallel reactions (20× wide field; tubulin probe only shown). Kinesin-5 was inhibited with 100 μM STLC. Dynein was inhibited with the CC1 fragment of dynactin (1 mg/ml). Note that STLC alone slightly accelerated initial aggregation, whereas CC1 slowed it considerably. (B) Final assemblies at 120 min from the reactions shown in A (40× confocal). In STLC alone, NUMA (blue) foci were on the inside and Aurora B (red) foci on the inside. In CC1 alone, minus ends and NUMA were less focused. In both inhibitors clusters of Aurora B foci were the dominant organizing feature. These combined with loose NUMA aggregates to organize microtubules into quasi-hexagonal arrays in some parts of the coverslip. The second panel in each pair is a 3× view of a region in the first panel. Each panel was normalized to 8 bits in each color channel to facilitate visualization of structure. This normalization overestimates local NUMA intensity in CC1 and CC1 + STLC, where it was much weaker than control and STLC alone. Aurora B foci were of similar intensity in all conditions.