Figure 1.
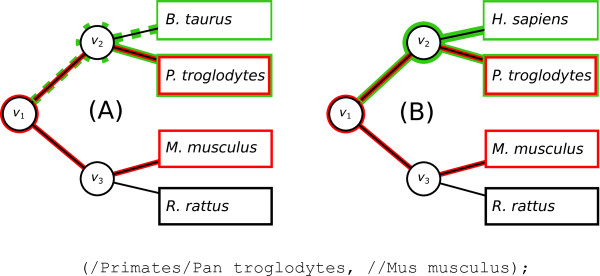
Example of a subtree constraint. In the pattern shown in the lower part of the figure, a constraint has been put on the node leading to P. troglodytes. The pattern is shown in red, and the subtree constraint is shown in green. This pattern with this constraint will find all the trees in which a subtree with sequences from P. troglodytes and M. musculus species are grouped. Non-Primates are forbidden from ν1, the common ancestor of P. troglodytes and M. musculus, to the node matching to P. troglodytes. Tree (A) is rejected, since the pattern does not allow B. taurus (which is not a Primate) to be in the subtree containing P. troglodytes (generated by ν1). On the other hand, tree (B) is accepted, as the subtree generated by ν1 contains only primates.
