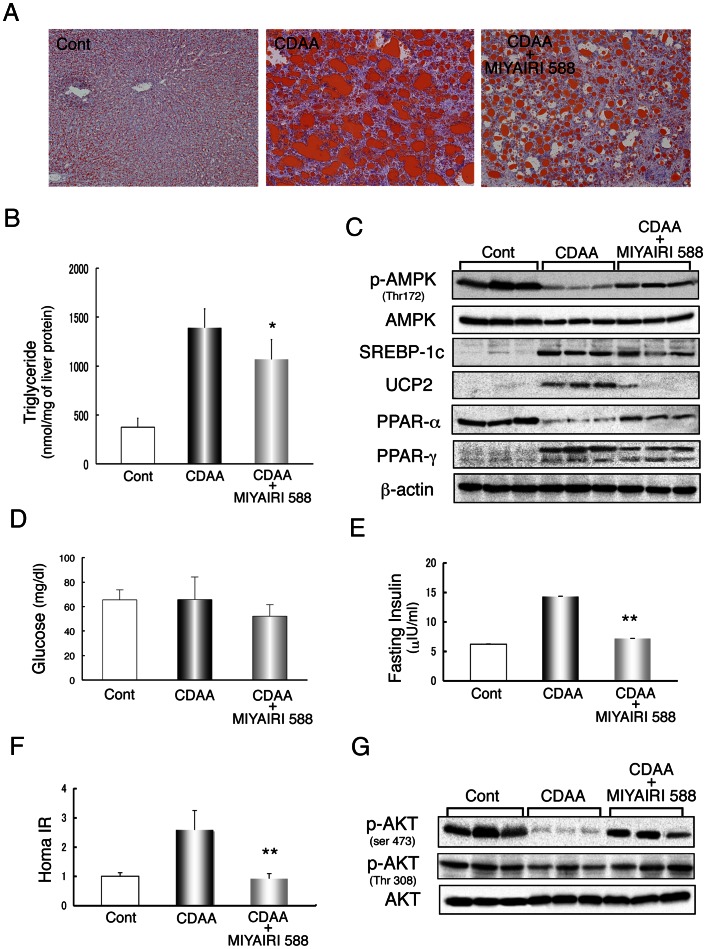
Figure 2. MIYAIRI 588 reduced hepatic lipid deposition and insulin resistance.
Male Fischer 344 rats (n = 6 per group) were fed a control (choline-sufficient/L-amino acid-defined CSAA) diet, choline-deficient/L-amino acid-defined (CDAA) diet, or CDAA diet plus MIYAIRI 588 for 8 weeks. MIYAIRI 588 was administered after CDAA diet feeding for 2 weeks, as described in the Materials and Methods. Cont, control. (A) Lipid accumulation was evaluated by oil red O staining of the liver sections. Data are representative of 6 individual liver sections. Original magnification, ×40. (B) Total triacylglycerol (TG) content in the liver was measured and normalized to protein concentration. Results represent mean ± SD values. *p<0.05 versus the CDAA-diet-fed group. (C) AMPK activation and lipogenesis- or lipolysis-related protein expression were detected by western blotting. β-actin expression was used as a loading control. (D) Fasting blood glucose levels, (E) Fasting plasma insulin levels, and (F) HOMA-IR were assessed in the rats. The data are shown as mean ± SD values. **p<0.01 vs. the CDAA-diet-fed group. (G) Total and phosphorylated AKT (Ser473 and Thr308) were represented under regular feed conditions.