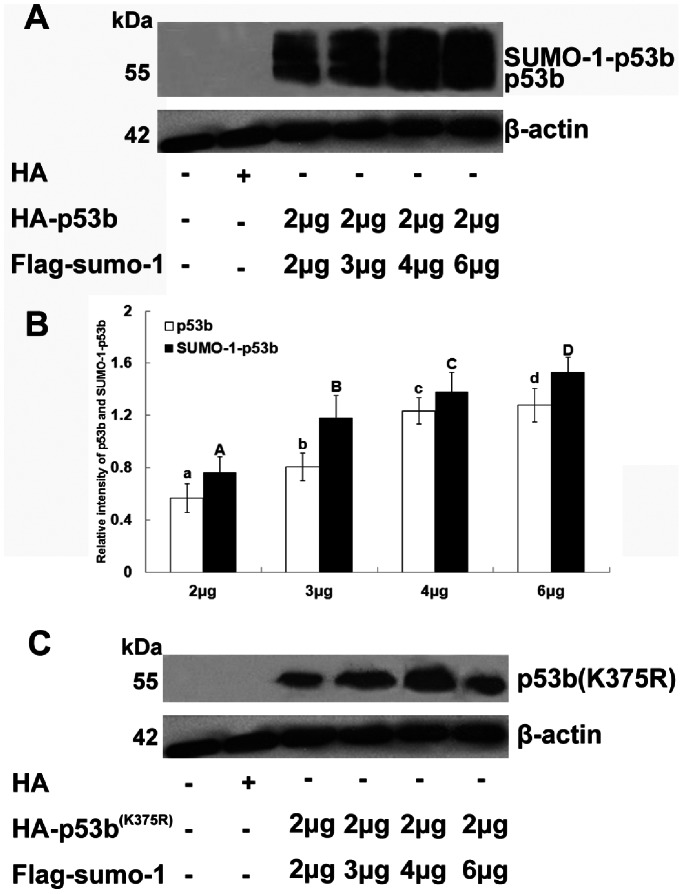
Figure 3. SUMO-1 modification enhanced the stability of p53b in a dose-dependent manner.
(A) Pre-GCs were co-transfected with 2 µg HA-p53b plasmid and different amounts (2 µg, 3 µg, 4 µg, and 6 µg) of Flag-sumo-1 plasmids. 20 µg total proteins were prepared and resolved by SDS–PAGE and analyzed by Western blot using anti-HA-specific antibody. Positions of molecular weight markers, free p53b and p53b-SUMO-1 conjugates are indicated. β-actin is a loading control. (B) Relative expression quantity of p53b and SUMO-1-p53b were determined by densitometric scans. The total amount of β-actin present in the lower set of lanes was used to standardize the amount of p53b and SUMO-1-p53b present in the upper set of lanes. The value expressed by each bar represents the mean ± SD (n = 3). Different letters indicated statistical difference (P<0.05). (C) Pre-GCs were co-transfected with 2 µg HA-p53b (K375R) and different amounts (2 µg, 3 µg, 4 µg, and 6 µg) of Flag-sumo-1 plasmids. HA antibody were used to detect the expression of p53b (K375R) after transfection. The results showed that elevating the amount of transfected Flag-sumo-1 resulted in a simultaneous increase in the level of SUMOylated p53b and free p53b, but not mutant p53b (K375R).