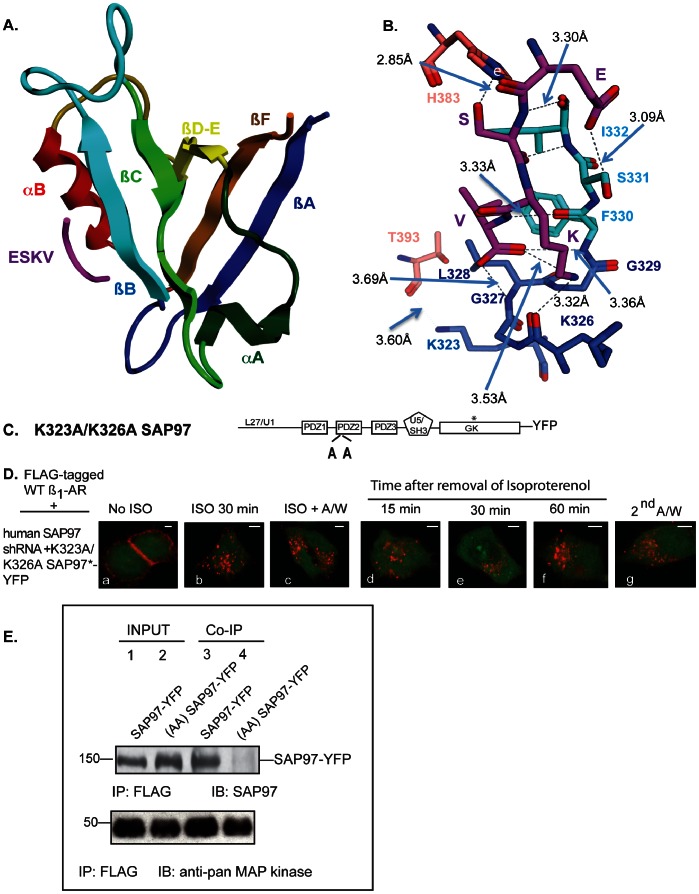
Figure 6. Lysines 323 and 326 in PDZ2 influence SAP97-mediated recycling and binding to the ß1-AR.
A, ribbon diagram of the SAP97 PDZ2 structure with ESKV peptide bound. In PDZ2 domain helixes and strands are named according to Doyle et al [45] and shown in different colors. ESKV peptide is shown in magenta. B, ligand binding interactions between the C-terminal sequence (ESKV) of the human ß1-AR and SAP97 PDZ2 domain. Amino acids representing different strands and helixes in PDZ2 domain structure are shown in different colors: ßC strand, green; ßB strand, light blue; ßA strand, dark blue; alpha/B helix, light red. ESKV sequence is shown in magenta, oxygen atoms are depicted in red, nitrogen atoms are in navy blue and hydrogen bonds are indicated as dashed blue lines. Distance between the alpha-carbons of amino acids is shown in Å. C, cartoon of the K323A/K326A PDZ2 mutant that was used in Panel D. D, effect of mutating K323 and K326 to Ala on SAP97-mediated regulation of ß1-AR recycling. HEK293 cells stably expressing the FLAG-tagged WT ß1-AR and hSAP97 shRNA were transfected with K323A/K326A SAP97-YFP and the internalization and recycling of the ß1-AR were analyzed as described in Fig. 2. Each scale bar represents 5 µm. E, Cells stably expressing FLAG ß1-AR and hSAP97 shRNA were transfected with SAP97-YFP or K323A/K326A SAP97-YFP. FLAG IP’s from cell extracts were subjected to Western blotting (IB) and probed with anti-SAP97 antibody or with anti-pan MAP kinase antibody.