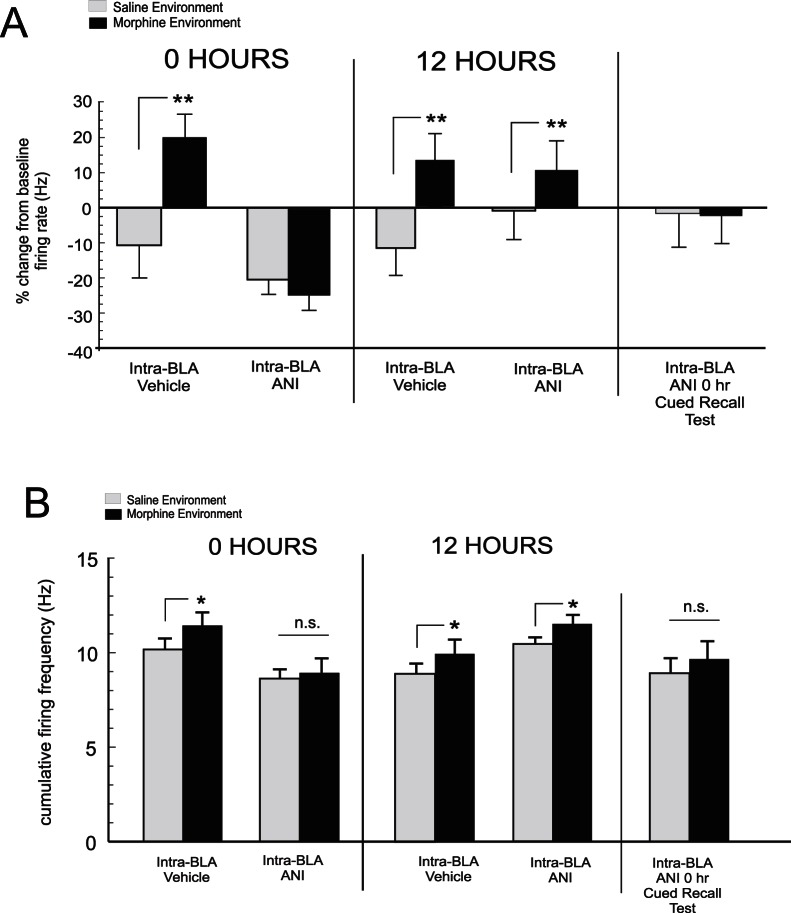
Figure 6. Effects of acute (0 hr) intra-BLA protein synthesis inhibition on mPFC neuronal associative morphine responses during CPP testing.
A, When administered at 0 hrs post-conditioning, intra-BLA ANI blocks mPFC neuronal encoding of associative opiate reward memory, demonstrated by a lack of associative firing activity increases during exposure to morphine environments during CPP testing or during a morphine cued recall CPP test. In contrast, vehicle controls at 0 or 12 hrs or intra-BLA ANI administration at 12 hrs, does not block mPFC neuronal encoding of opiate reward memory, demonstrated by robust mPFC neuronal firing activity during CPP exposure to morphine-paired environments. B, Cumulative mPFC neuronal firing frequency rates are presented for the same experimental groups shown in panel A. Cumulative neuronal firing frequency demonstrates morphine-environment specific associative increases in firing rates relative to saline-paired environments in groups receiving intra-BLA vehicle at 0 or 12 hrs post-conditioning or in rats receiving intra-BLA anisomycin at 12 hrs post-conditioning. However, this associative increase in firing activity is absent in rats receiving intra-BLA anisomycin at 0 hrs post-conditioning.