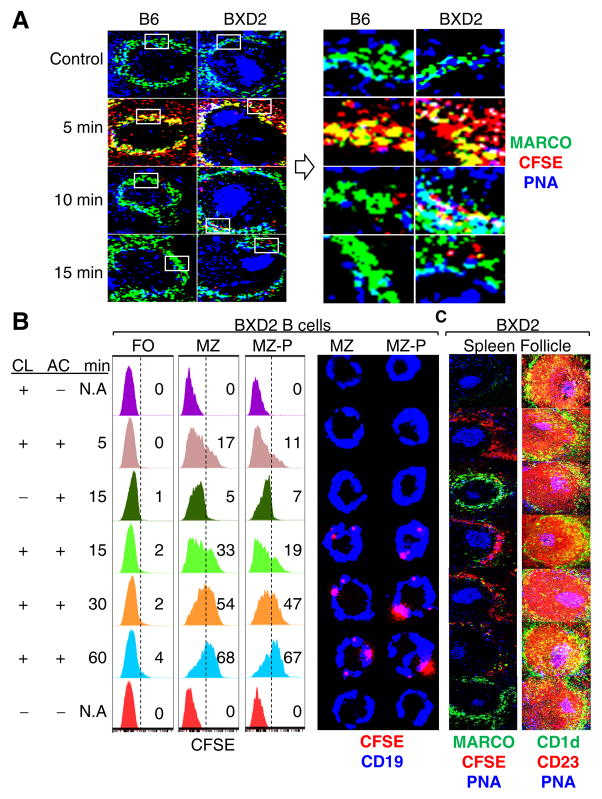
Figure 2.
Defective clearance of apoptotic debris is associated with increased uptake of apoptotic cells by MZ/FO shuttling MZ-P B cells in the spleens of BXD2 mice. (A) Left: Confocal imaging showing the kinetics of clearance of administered CFSE-labeled apoptotic thymocytes (pseudo color red) in the MZ area in the spleen of 2-mo-old mice. Right: High power view of the indicated (box) areas in the left panels. (B, C) BXD2 mice (2-mo) were treated with either CL- or PBS-liposome 4 hrs prior to CFSE-labeled apoptotic thymocyte administration. Following AC administration, mice were sacrificed at the indicated time points (min). (B) Left: FACS analysis of subpopulations of B cells that were positive for AC Ags (CFSE+). FO, MZ, and MZ-P B cells were gated as described (17, 18). Right: Confocal imaging assessment of the binding of FACS sorted MZ or MZ-P B cells with CFSE+ (pseudo color red) apoptotic debris. A representative cell from the indicated subset is shown. (C) Confocal imaging showing a representative spleen follicle from each group to reveal the clearance of the administered CFSE+ apoptotic thymocytes (pseudo color red) in the spleen (left) and the anatomic location of FO (red: CD1d− CD23+), MZ (green: CD1d+CD23−), MZ-P (yellow: CD1d+CD23+), and GC (blue: PNA+) in each group (right) (N=2–3 mice per group for 3 independent experiments).