Abstract
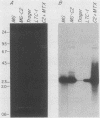
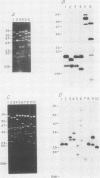
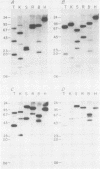
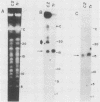
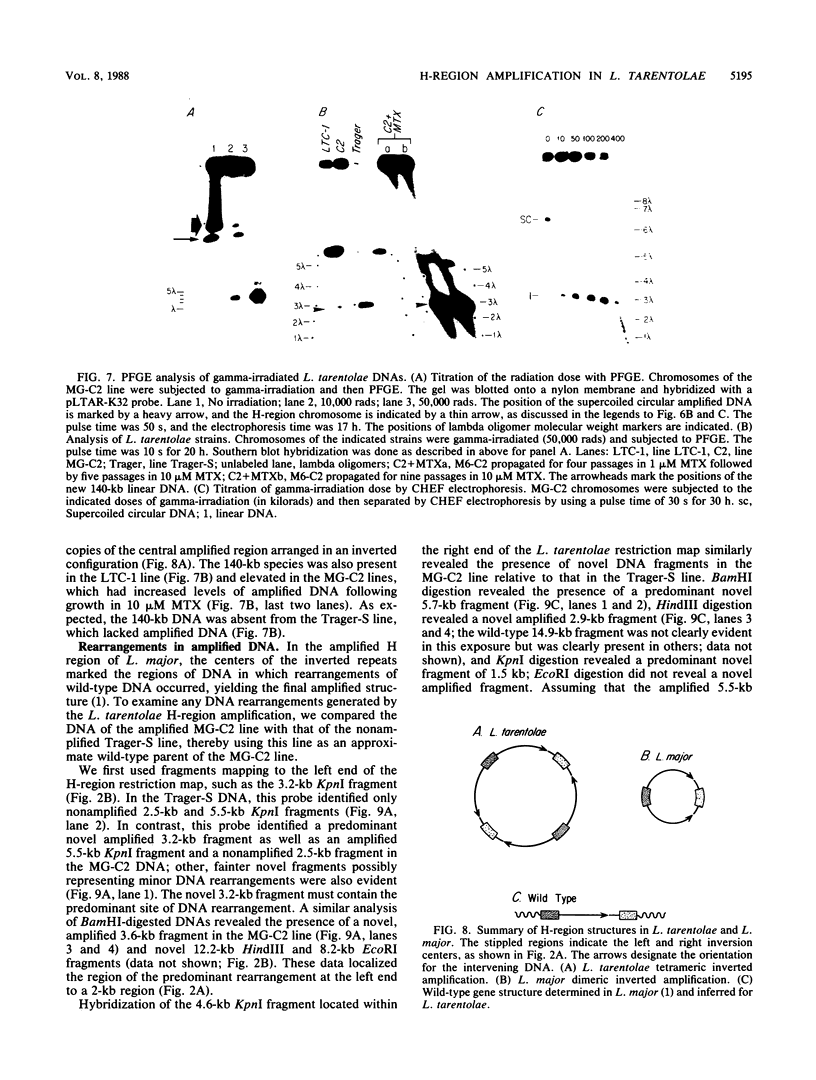
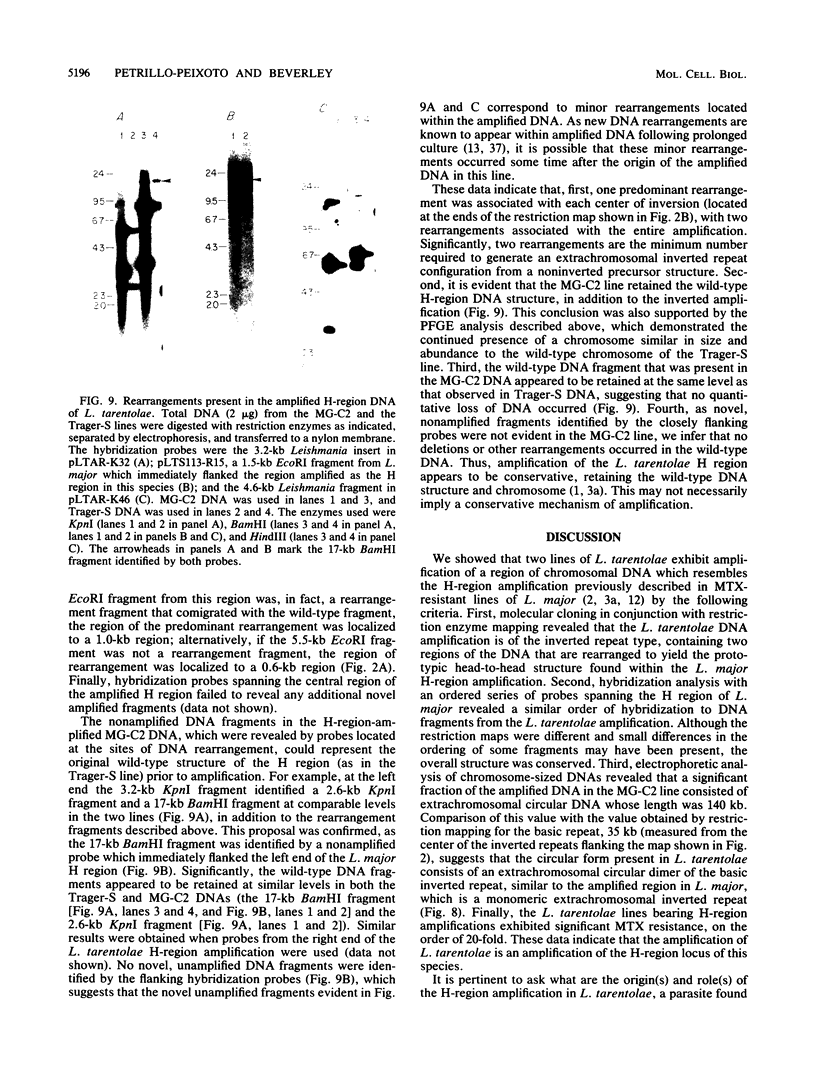
We describe the structure of amplified DNA that was discovered in two laboratory stocks of the protozoan parasite Leishmania tarentolae. Restriction mapping and molecular cloning revealed that a region of 42 kilobases was amplified 8- to 30-fold in these lines. Southern blot analyses of digested DNAs or chromosomes separated by pulsed-field electrophoresis showed that the amplified DNA corresponded to the H region, a locus defined originally by its amplification in methotrexate-resistant Leishmania major (S. M. Beverley, J. A. Coderre, D. V. Santi, and R. T. Schimke, Cell 38:431-439, 1984). Similarities between the amplified DNA of the two species included (i) extensive cross-hybridization; (ii) approximate conservation of sequence order; (iii) extrachromosomal localization; (iv) an overall inverted, head-to-head configuration as a circular 140-kilobase tetrameric molecule; (v) two regions of DNA sequence rearrangement, each of which was closely associated with the two centers of the inverted repeats; (vi) association with methotrexate resistance; and (vii) phenotypically conservative amplification, in which the wild-type chromosomal arrangement was retained without apparent modification. Our data showed that amplified DNA mediating drug resistance arose in unselected L. tarentolae, although the pressures leading to apparently spontaneous amplification and maintenance of the H region are not known. The simple structure and limited extent of DNA amplified in these and other Leishmania lines suggests that the study of gene amplification in Leishmania spp. offers an attractive model system for the study of amplification in cultured mammalian cells and tumors. We also introduced a method for measuring the size of large circular DNAs, using gamma-irradiation to introduce limited double-strand breaks followed by sizing of the linear DNAs by pulsed-field electrophoresis.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beverley S. M. Characterization of the 'unusual' mobility of large circular DNAs in pulsed field-gradient electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):925–939. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beverley S. M., Coderre J. A., Santi D. V., Schimke R. T. Unstable DNA amplifications in methotrexate-resistant Leishmania consist of extrachromosomal circles which relocalize during stabilization. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):431–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90498-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beverley S. M., Ellenberger T. E., Cordingley J. S. Primary structure of the gene encoding the bifunctional dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase of Leishmania major. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2584–2588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beverley S. M., Ismach R. B., Pratt D. M. Evolution of the genus Leishmania as revealed by comparisons of nuclear DNA restriction fragment patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):484–488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. M., DeRose M. L., Gaudray P., Moore C. M., Needham-Vandevanter D. R., Von Hoff D. D., Wahl G. M. Double minute chromosomes can be produced from precursors derived from a chromosomal deletion. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1525–1533. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. M., Gaudray P., De Rose M. L., Emery J. F., Meinkoth J. L., Nakkim E., Subler M., Von Hoff D. D., Wahl G. M. Characterization of an episome produced in hamster cells that amplify a transfected CAD gene at high frequency: functional evidence for a mammalian replication origin. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1740–1750. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coderre J. A., Beverley S. M., Schimke R. T., Santi D. V. Overproduction of a bifunctional thymidylate synthetase-dihydrofolate reductase and DNA amplification in methotrexate-resistant Leishmania tropica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2132–2136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detke S., Chaudhuri G., Kink J. A., Chang K. P. DNA amplification in tunicamycin-resistant Leishmania mexicana. Multicopies of a single 63-kilobase supercoiled molecule and their expression. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3418–3424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewes H., Ostergaard H. L., Simpson L. Impaired drug uptake in methotrexate resistant Crithidia fasciculata without changes in dihydrofolate reductase activity or gene amplification. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1986 May;19(2):149–161. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(86)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberger T. E., Beverley S. M. Biochemistry and regulation of folate and methotrexate transport in Leishmania major. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10053–10058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberger T. E., Beverley S. M. Reductions in methotrexate and folate influx in methotrexate-resistant lines of Leishmania major are independent of R or H region amplification. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13501–13506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federspiel N. A., Beverley S. M., Schilling J. W., Schimke R. T. Novel DNA rearrangements are associated with dihydrofolate reductase gene amplification. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9127–9140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fojo A., Akiyama S., Gottesman M. M., Pastan I. Reduced drug accumulation in multiply drug-resistant human KB carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1985 Jul;45(7):3002–3007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford M., Fried M. Large inverted duplications are associated with gene amplification. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):425–430. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90328-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadler H. Nucleic acid hybridization for measurement of effects of antiviral compounds on human cytomegalovirus DNA replication. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Sep;24(3):370–374. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.3.370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey E. P., Coderre J. A., Santi D. V. Selection and properties of Leishmania tropica resistant to 10-propargyl-5,8-dideazafolate, an inhibitor of thymidylate synthetase. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1985 Oct;17(1):79–91. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(85)90129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey E. P., Santi D. V. Stable amplified DNA in drug-resistant Leishmania exists as extrachromosomal circles. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):535–540. doi: 10.1126/science.3726545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Eichelmann M. C., Holz G., Jr, Beach D., Simpson A. M., Simpson L. Comparison of several lizard Leishmania species and strains in terms of kinetoplast minicircle and maxicircle DNA sequences, nuclear chromosomes, and membrane lipids. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Jan 15;27(2-3):143–158. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumont R., Washtien W. L., Caput D., Santi D. V. Bifunctional thymidylate synthase-dihydrofolate reductase from Leishmania tropica: sequence homology with the corresponding monofunctional proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5387–5391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlin J. L., Milbrandt J. D., Heintz N. H., Azizkhan J. C. DNA sequence amplification in mammalian cells. Int Rev Cytol. 1984;90:31–82. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61487-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hightower R. C., Metge D. W., Santi D. V. Plasmid migration using orthogonal-field-alternation gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8387–8398. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes D. E., Simpson L. Introduction of plasmid DNA into the trypanosomatid protozoan Crithidia fasciculata. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6058–6062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson F. Chemical changes induced in DNA by ionizing radiation. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1985;32:115–154. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60347-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iovannisci D. M., Goebel D., Allen K., Kaur K., Ullman B. Genetic analysis of adenine metabolism in Leishmania donovani promastigotes. Evidence for diploidy at the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14617–14623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kink J. A., Chang K. P. Tunicamycin-resistant Leishmania mexicana amazonensis: expression of virulence associated with an increased activity of N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase and amplification of its presumptive gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1253–1257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leon W., Fouts D. L., Manning J. Sequence arrangement of the 16S and 26S rRNA genes in the pathogenic haemoflagellate Leishmania donovani. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Feb;5(2):491–504. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.2.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Looney J. E., Hamlin J. L. Isolation of the amplified dihydrofolate reductase domain from methotrexate-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):569–577. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer B. J., Lai E., Hamkalo B. A., Hood L., Attardi G. Novel submicroscopic extrachromosomal elements containing amplified genes in human cells. Nature. 1987 Jun 4;327(6121):434–437. doi: 10.1038/327434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. R., Ling V. Genetic and biochemical characterization of multidrug resistance. Pharmacol Ther. 1985;28(1):51–75. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(85)90082-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T. Gene amplification in cultured animal cells. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):705–713. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90406-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T. Gene amplification in cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):5989–5992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T., Sherwood S. W., Hill A. B., Johnston R. N. Overreplication and recombination of DNA in higher eukaryotes: potential consequences and biological implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2157–2161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. M., Feagin J. E., Stuart K., Simpson L. Editing of kinetoplastid mitochondrial mRNAs by uridine addition and deletion generates conserved amino acid sequences and AUG initiation codons. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):401–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90160-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L. The mitochondrial genome of kinetoplastid protozoa: genomic organization, transcription, replication, and evolution. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:363–382. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.002051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G. R. DNA amplification in drug resistant cells and in tumours. Cancer Surv. 1986;5(1):1–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Gene amplification. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:447–491. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tait A. Sexual processes in the kinetoplastida. Parasitology. 1983 Apr;86(Pt 4):29–57. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000050836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Cornelissen A. W., Barry J. D., Borst P. Chromosomes of kinetoplastida. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3109–3115. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02266.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R., Borst P. Antigenic variation in Trypanosoma brucei analyzed by electrophoretic separation of chromosome-sized DNA molecules. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90302-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. On the possibility of metabolic control of replicon "misfiring": relationship to emergence of malignant phenotypes in mammalian cell lineages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3673–3677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallbanks K. R., Maazoun R., Canning E. U., Rioux J. A. The identity of Leishmania tarentolae Wenyon 1921. Parasitology. 1985 Feb;90(Pt 1):67–78. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000049027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]