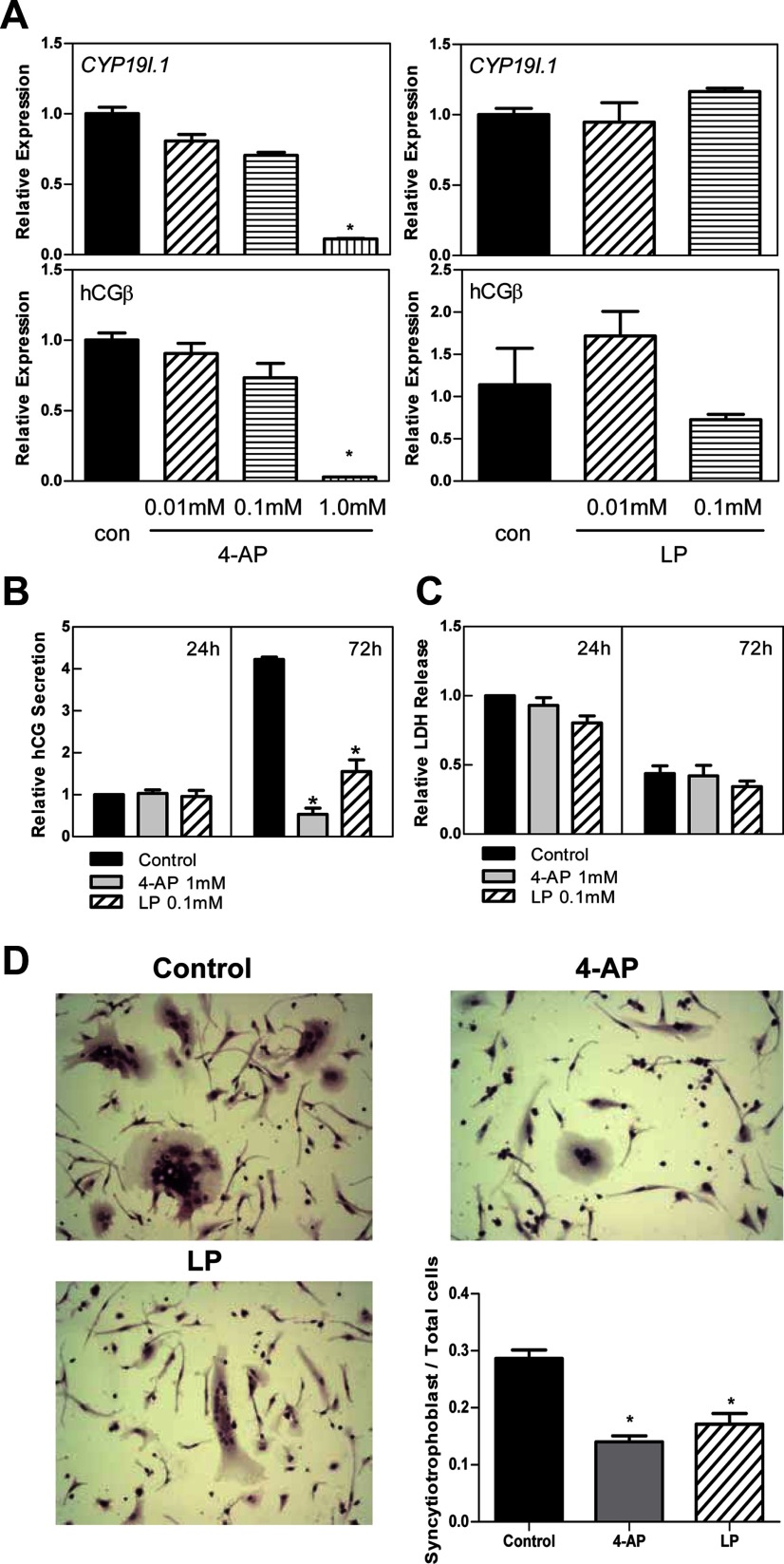
Figure 5.
Voltage-gated K+ channel blockers inhibit differentiation of human trophoblast cells. A, Freshly isolated human placental cytotrophoblasts were treated with voltage-gated K+ channel blocker 4-AP (0.01 mM, 0.1 mM, or 1 mM), KV7 channel blocker LP (0.01 mM or 0.1 mM), or ethanol (con) for 72 hours. RNA was isolated from cells after treatment, and the expression of CYP19I.1 and hCGβ mRNA was analyzed by qRT-PCR; RPLP0 was used as the internal reference. *, Significantly different (P < .05) from values of cells treated with ethanol. B and C, Culture medium was collected 24 and 72 hours after the initiation of treatment with 4-AP (1 mM), LP (0.1 mM), or ethanol (control), and assayed for secreted hCG using ELISA (B) or LDH release using a cytotoxicity detection kit (C). Data are the mean ± SEM of values from 3 independent experiments, each conducted in duplicate, and are expressed relative to the 24-hour control. *, Significantly different (P < .05) from control. D, After 72 hours of treatment with 4-AP (1 mM), LP (0.1 mM), or ethanol (control), the cells were stained with hematoxylin and eosin and viewed by light microscopy (×200). ImageJ was used to quantify the percentage of clustered cells relative to total cell number in 8 different fields from 2 independent experiments performed in duplicate. *, Significantly (P < .05) decreased compared with control.