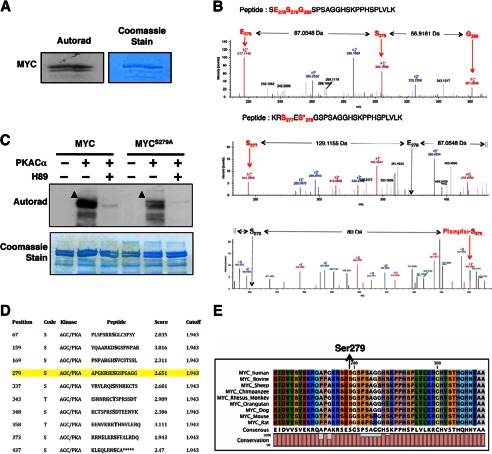
FIGURE 2.
PKA phosphorylates MYC at Ser-279. A, PKACα phosphorylates MYC in vitro. B, PKACα phosphorylates MYC at Ser-279. Top, LC-MS2 spectra of the peptide SESGSPSAGGHSKPPHSPLVLK from nonphosphorylated recombinant MYC are shown. A region spanning Ser-279 is shown to reveal the nonphosphorylated state at Ser-279. The b ions corresponding to Glu-278 and Ser-279 are labeled using red arrows. The corresponding amino acid in the peptide is also labeled in red. The mass difference between these ions is also indicated. A complete list of ions for the given peptide is listed in supplemental Table S1. Bottom panels, LC-MS2 spectra of the peptide RSESGSPSAGGHSKPPHSPLVLK from PKA-phosphorylated recombinant MYC is shown. A region spanning Ser-279 is shown to reveal the phosphorylated state at Ser-279.The b ions corresponding to Ser-277 and phosphorylated Ser-279 (also designated by an asterisk) are labeled using a red arrow. The corresponding amino acid in the peptide is also labeled in red. The positions of the hypothetical Glu-278 and nonphosphorylated Ser-279 ion are indicated by the black arrow. The mass difference between these ions is also indicated. A mass increase of 80 Da was observed in the phosphorylated peptide, demonstrating that Ser-279 is phosphorylated. A complete list of ions for the given peptide is listed in supplemental Table S2. C, mutating Ser-279 to alanine diminished MYC phosphorylation by PKA in vitro. Addition of H89 completely abolished phosphorylation of MYC by PKA. Arrowheads indicate phosphorylated MYC. D, PKA phospho-acceptor sites on MYC are predicted by in silico phosphorylation prediction tool GPS 2.0 (43). Ser-279 is a predicted phospho-acceptor site of PKA on MYC (highlighted in yellow). E, the region containing Ser-279 in MYC is evolutionarily conserved across species.