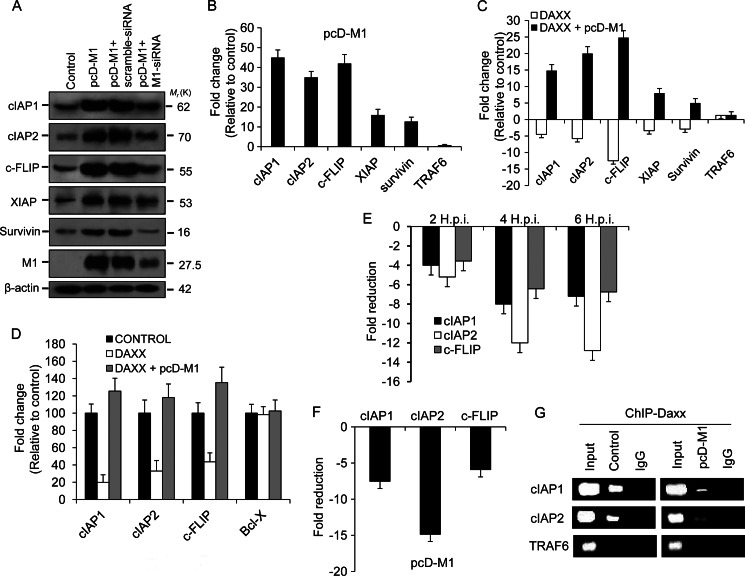
FIGURE 3.
Prevention of Daxx promoter binding by M1 activates antiapoptotic genes. A, immunoblot analysis of cIAP1, cIAP2, cFLIP, XIAP, and survivin was performed after 293T cells were transfected or mock-transfected with pcD-M1 along with scrambled siRNA or M1 siRNA (60 nmol) and left untreated for 36 h. The effect of M1 siRNA was assessed by measuring M1 expression levels in M1 siRNA- or scrambled siRNA-transfected cells. β-Actin served as an internal loading control. B, transcript levels of the cIAP1, cIAP2, cFLIP, XIAP, survivin, and TRAF6 genes were analyzed by Q-PCR using SYBR Green from lysates of 293T cells after transient transfection with pcD-M1 and left untreated for 36 h. GAPDH was used as a reference gene. TRAF6 was analyzed as a negative control for the RelB-responsive genes. Data are presented as -fold change (based on 2ΔΔCt values) relative to non-infected control cells (mean ± S.D.; n = 3). C, 293T cells were transfected with pcD-Daxx or co-transfected with pcD-Daxx and pcD-M1 constructs, and after 36 h, transcripts of cIAP1, cIAP2, cFLIP, XIAP, survivin, and TRAF6 genes were analyzed by Q-PCR. GAPDH was used as a reference gene. Results are representative of three independent experiments. Values represent means ± S.D. of the experiment with three measurements taken. D, 293T cells (85–90% confluent in 12-well plates) were transiently transfected with pcDNA6-RelB, pcDNA6-Daxx, Renilla luciferase reporter (pRL-TK), and either cIAP1-pGL3-basic, cIAP2-pGL3-basic, cFlip-pGL3-basic, or BCL-X-pGL3 (cloned promoters) and/or pcD-M1. The ratio of experimental vector to co-reporter vector (Renilla luciferase) was 10:1. Luciferase assays were performed 24 h posttransfection. Bcl-x gene promoter served as a control. All assays were performed in triplicate. E and F, chromatin was immunoprecipitated using anti-Daxx antibody or control IgG antibodies to determine association of Daxx with RelB candidate target gene promoters (cIAP1, cIAP2, and cFLIP) after A549 cells were infected with PR8 (1 m.o.i.) strain for the given time points (2, 4, and 6 h.p.i.) or after 293T cells were transfected with pcD-M1 and left untreated for 36 h. Target gene promoters were amplified by Q-PCR (40 cycles) using promoter-specific primers that encompassed NF-κB binding sites. Values represent averages of three Q-PCRs from three ChIP experiments. G, 293T cells were transiently transfected with pcD-M1 and left untreated for 36 h before chromatin was precipitated using anti-Daxx antibody, and recovered promoters were amplified by Q-PCR (40 cycles) using primers for the cIAP1, cIAP2, and TRAF6 promoters and then analyzed by gel electrophoresis. TRAF6 gene promoter served as a control. Input represents 10% of the chromatin specimen directly analyzed by Q-PCR without immunoprecipitation. Error bars represent S.D.