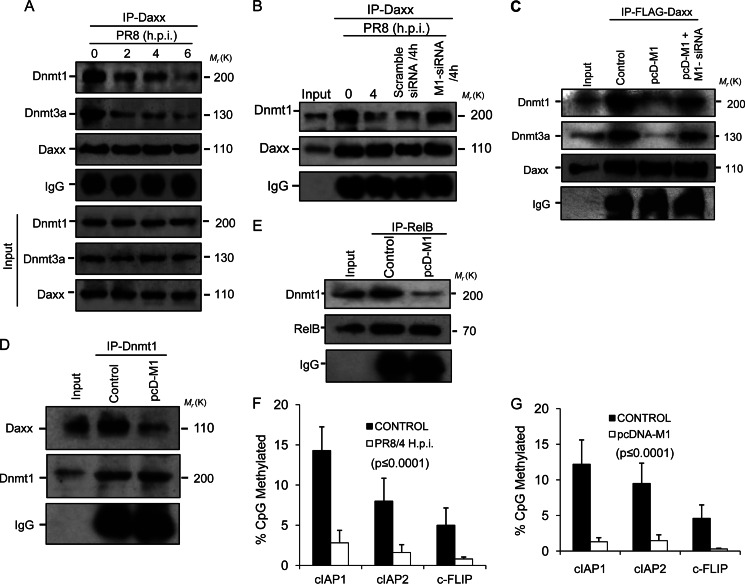
FIGURE 4.
Methylation of target promoters decreases as M1 prevents Dnmts from binding Daxx. A, A549 cells were infected with PR8 (1 m.o.i.) strain for the given time points (0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 h.p.i.) before cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using anti-Daxx antibody followed by immunoblotting with Dnmt1 and Dnmt3a antibodies. IgG served as a loading control, and input lysate (PR8-infected cell lysate without immunoprecipitation (IP)) was used for antibody specificity. B, to analyze the role of M1 in disruption of Daxx-Dnmt association, A549 cells were transfected with scrambled siRNA or M1-specific siRNA (60 nmol) prior to PR8 infection (1 m.o.i., 4 h.p.i.), and cell lysates of infected (0 and 4 h.p.i.) and siRNA-treated infected (4 h.p.i.) cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-Daxx antibody followed by immunoblotting with Dnmt1 antibody. Cell lysate without immunoprecipitation was used as input. C, 293T cells were co-transfected with pFLAG-Daxx and pcD-M1 after the cells were transfected or not with M1 siRNA (60 nmol). After 24 h of transfection, the whole cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG antibody followed by immunoblotting with Dnmt1 and Dnmt3a antibodies. Only pFLAG-Daxx-transfected cell lysates served as a control, and lysate without immunoprecipitation served as input. D, 293T cells were transfected or not (Control) with pcD-M1 and left untreated for 36 h before the cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Dnmt1 antibody followed by immunoblotting with anti-Daxx antibody. IgG served as a loading control, and total cell lysate was used as input. E, to detect Dnmt1 complexed with RelB in the presence of M1, RelB was immunoprecipitated (36 h posttransfection) with anti-RelB antibody using control and M1-overexpressing (pcD-M1-transfected) 293T cell lysates followed by immunoblotting with anti-Dnmt1. F and G, genomic DNA from control and PR8-infected (1 m.o.i., 4 h.p.i.) A549 cells and control and pcD-M1-transfected 293T cells was isolated and treated with bisulfite, and 0.5 μg was amplified by PCR, cloned, and sequenced (cIAP1, cIAP2, and cFLIP promoters). The methylation profile of the promoters was determined by comparing the sequence of bisulfite-converted DNA with unmodified DNA. The percentage of methylated CpG sites is shown for each promoter examined. The values represent a significance value of p ≤ 0.0001. Error bars represent S.D.