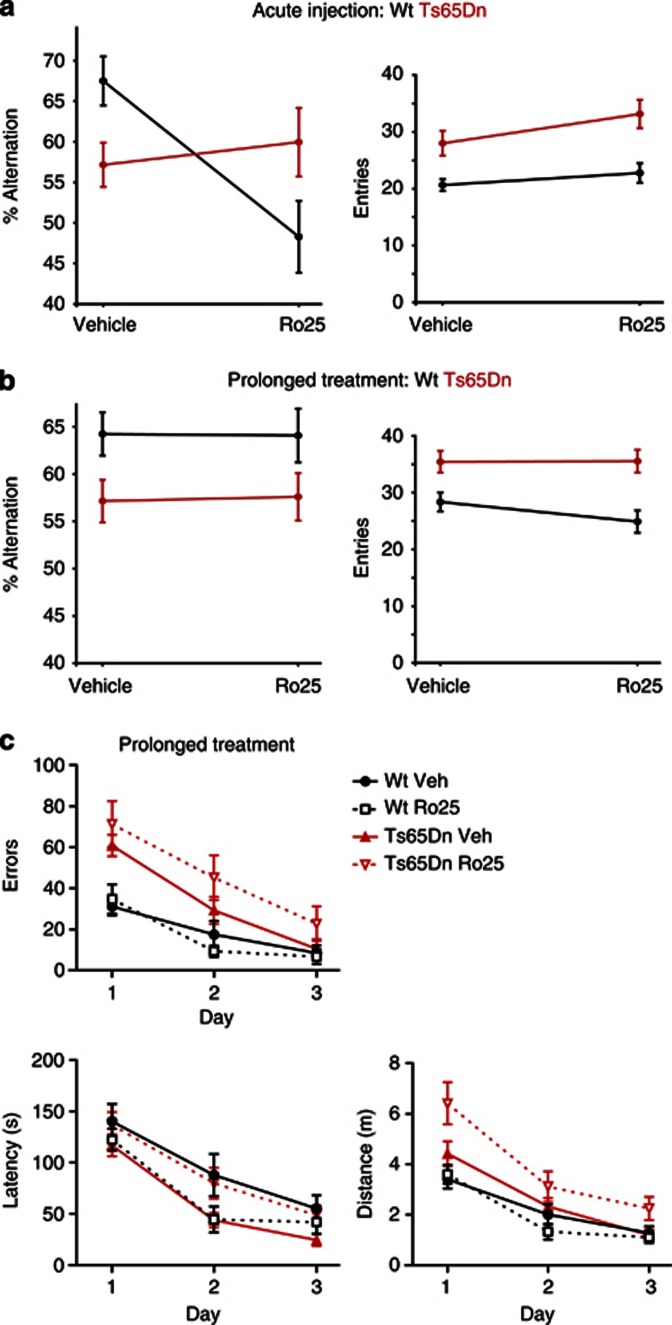
Figure 7.
Ro25-6981 (Ro25) dosing differentially affects cognitive behaviors in wild-type (wt) and Ts65Dn mice, depending on dosing regimen (acute vs prolonged). (a) Y-maze alternations and entries are shown following acute Ro25 treatment. There was a significant genotype × treatment effect on the Y-maze alternations following acute Ro25 treatment (p<0.005; n=14/12 Ts65Dn and 14/13 wt vehicle/Ro25). Vehicle-treated Ts65Dn mice were impaired in percent alternations compared with wt mice (p<0.05), indicating a deficit in Ts65Dn mice. However, Ro25-treated wt mice exhibited significantly impaired alternations compared with Ro25-treated Ts65Dn mice (p<0.05). This was due to a significant impairment of alternations in Ro25-treated wt mice compared with vehicle-treated wt mice (p<0.05), and no significant effect of Ro25 treatment on Ts65Dn mice. Although there was an effect of genotype on arm entries (p<0.0001) reflecting increased activity of Ts65Dn mice, there were no genotype × treatment or treatment effects on arm entries. (b) Y-maze alternations and entries are shown following prolonged Ro25 dosing. There was an effect of genotype (p<0.01; n=20/19 Ts65Dn and 20/18 wt vehicle/ Ro25), with the Ts65Dn mice showing impaired alternations compared with wt mice, but there were no treatment or genotype × treatment effects on alternations. There was also an effect of genotype on arm entries (p<0.0001), with more arm entries in Ts65Dn mice than in wt mice, but there were no treatment or genotype × treatment effects on entries. (c) Barnes maze performance across 3 days of training is shown following prolonged Ro25 dosing. All groups learned the task with improved latency, distance, and error levels across days of training (p<0.0001; n=10/9 Ts65Dn and 9/8 wt vehicle/Ro25), but Ts65Dn mice showed significant impairments in both distance (p<0.01) and errors (p<0.0001) compared with wt mice. Significant genotype × treatment effects were observed for latency (p<0.05) and distance (p<0.05). This reflected a significantly increased latency (p<0.05) and distance (p<0.05) in Ro25-treated Ts65Dn mice compared with vehicle-treated Ts65Dn mice, whereas Ro25 treatment did not significantly affect wt mice. All data is shown as mean±SEM.