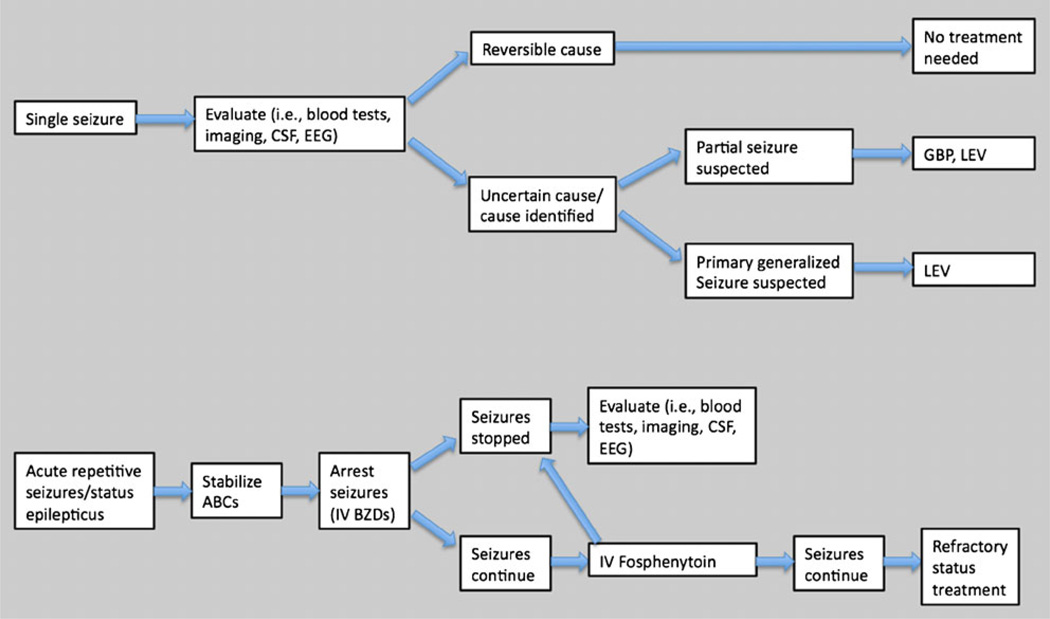
Figure 1.
Algorithm for treatment of seizures in transplant patients. Treatment of seizures in transplant patients must take into account the transplanted organ and antirejection comedications so that antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) do not place the transplanted organ at further risk. For single partial-onset or secondary generalized tonic-clonic seizures, investigation for an underlying symptomatic etiology should be promptly undertaken, and treatment may be deferred if a correctable etiology is determined and seizures do not recur. If seizures recur, or when seizure recurrence risk is uncertain or an underlying epileptogenic cause is found, treatment with levetira-cetam or gabapentin should be initiated as appropriate for suspected seizure type. For status epilepticus or acute repetitive seizures, intravenous lorazepam, followed, if necessary, by fosphenytoin should be administered. ABCs airway, breathing, and circulation; BZD benzodiazepine; CSF cerebrospinal fluid; EEG electroencephalography; GBP gabapentin; IV intravenous; LEV levetiracetam.