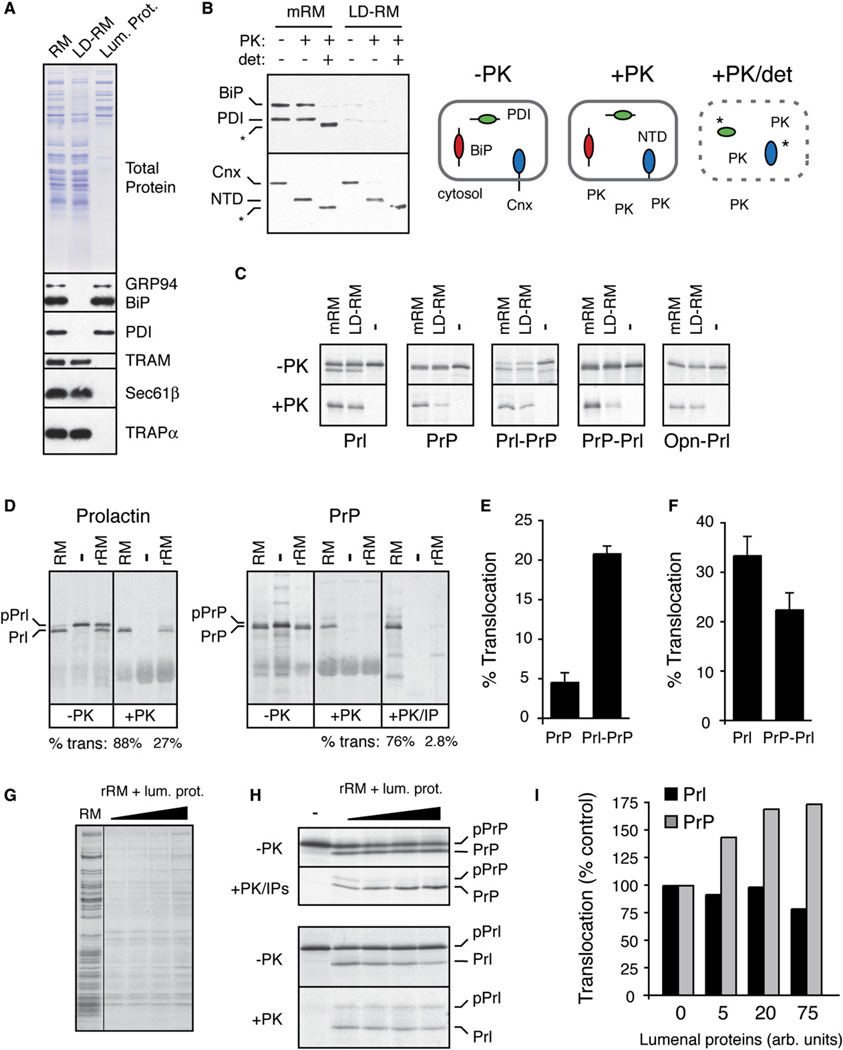
Figure 6. Reconstitution of Signal Sequence-Specific Translocational Attenuation In Vitro.
(A) Selective removal of lumenal proteins from rough microsomes (RM) by treatment with 0.075% deoxyBigCHAP. Equivalent aliquots of RM, the lumenal protein-depleted RM (LD-RM), and lumenal protein fraction were analyzed by Comassie staining (top) and immunoblots for various lumenal and membrane proteins (bottom). Although not seen in this blot, semiquantitative blotting showed ~80%–90% depletion of BiP and PDI (data not shown).
(B) Analysis of LD-RM and mock-extracted RM (mRM) for vesicle integrity and orientation by a protease protection assay. LD-RM and mRM were digested with Proteinase K (PK) in the absence or presence of detergent (det; 0.5% Triton X-100) and analyzed by immunoblotting for the N terminus of calnexin (Cnx), BiP, and PDI. The N-terminal lumenal domain of Cnx is indicated by NTD. Asterisks indicate core domains of Cnx and PDI that are resistant to complete protease digestion. A schematic of the results is shown.
(C) Analysis of protein translocation into mRM and LD-RM. The indicated constructs were translated in vitro without (−) or with membranes (either mRM or LD-RM) and analyzed for translocation by protease protection. Aliquots of the samples before and after PK digestion are shown. The relative translocation efficiency in LD-RM (relative to translocation in mRM) is indicated for each construct. All translation reactions contained a peptide inhibitor of glycosyation to simplify the analysis.
(D) Analysis of protein translocation in RM and rRM (proteoliposomes reconstituted from a total membrane protein extract of RM) as in (C). An aliquot of the PrP samples was also immunoprecipitated with anti-PrP (+PK/IP) to better visualize the translocation products. Translocation efficiencies are given below the lanes. The positions of precursor and processed products for Prl and PrP are indicated.
(E and F) The relative translocation efficiencies of the indicated constructs were analyzed in rRM and quantified from five experiments (mean ± SD). All constructs were translocated into RM with greater than 75% efficiency (data not shown).
(G) Coomassie stain of rRM reconstituted in the presence of increasing concentrations of lumenal proteins. Note that the concentration of lumenal proteins incorporated into the rRM is low and does not approach that found in RM (Supplemental Data, Note 5).
(H) Translocation of PrP and Prl was analyzed as in (D) using rRM containing increasing amounts of lumenal proteins. Note that in rRM, signal sequence cleavage is not complete, resulting in some translocation (and hence protease protection) of unprocessed protein.
(I) The experiment in (H) was quantified, normalized to translocation in rRM (lacking lumenal proteins), and graphed.