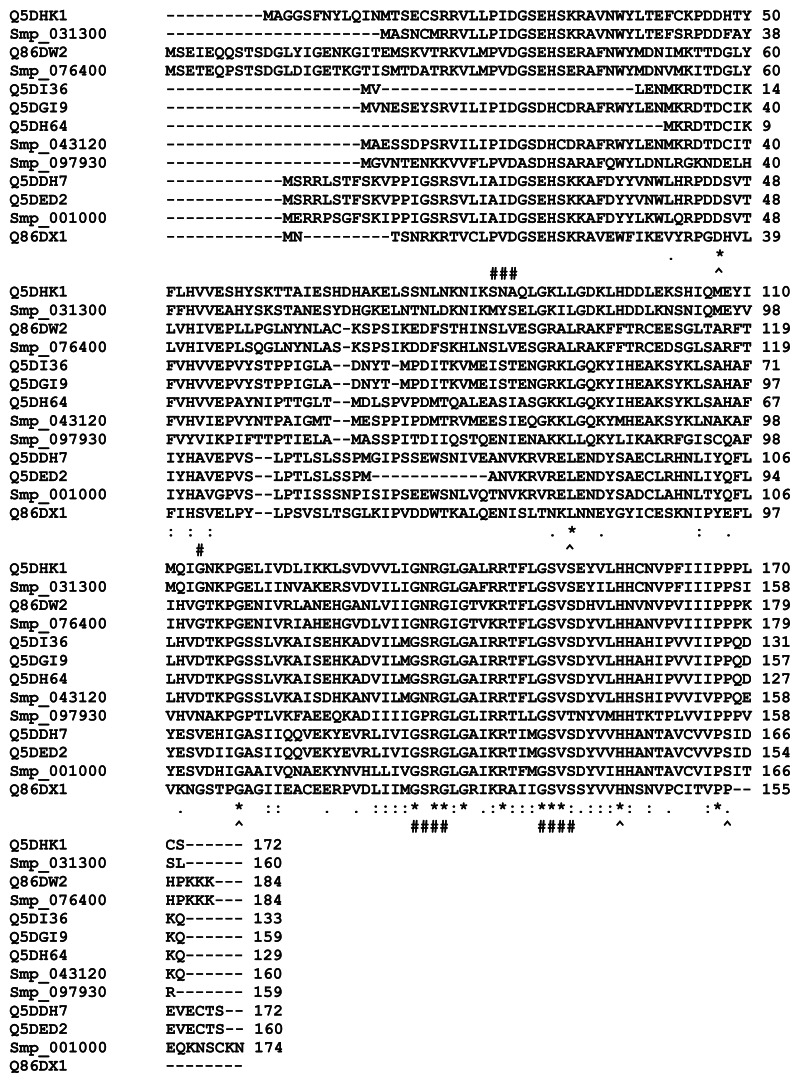
Figure 4.
Multiple sequence alignment of the sequences of selected universal stress proteins of Schistosoma mansoni and Schistosoma japonicum.
Notes: The sequence alignment of the 13 sequences with ATP-binding motif [G2XG9XG(S/T)] was generated using ClustalW (Larkin et al).56 Sequences of S. mansoni have “Smp” in the sequence identifier. The ligand binding sites (functional sites), annotated in the Conserved Domain Database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/cdd.shtml) are labeled with hashes (#). An observation is that aspartate, leucine, glycine, histidine, and proline residues are conserved in all the sequences (denoted by ^). The conserved positions are 57, 101, 127, 166, and 176 in Smp_076400 from S. mansoni. The conserved residues could be common functional sites for biochemical or environmental regulation of Schistosoma universal stress proteins. Meaning of alignment symbols: “*”, residues in column are identical; “:”, conserved substitutions; “.”, semiconserved substitutions. A visual analytics resource that can be used to interact with data is available at http://public.tableausoftware.com/views/schisto_features_usp/usp_align.
Abbreviations: ATP, adenosine triphosphate; D, aspartate; G, glycine; H, histidine; L, leucine; P, proline; Uniprot, Universal Protein Resource; USP, universal stress protein.