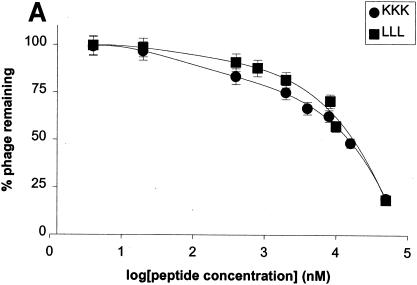
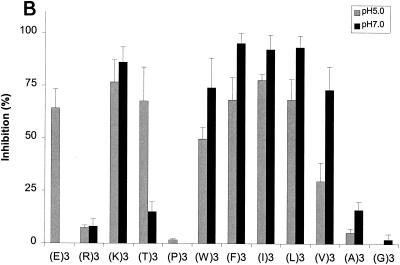
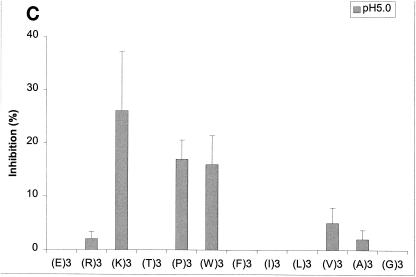
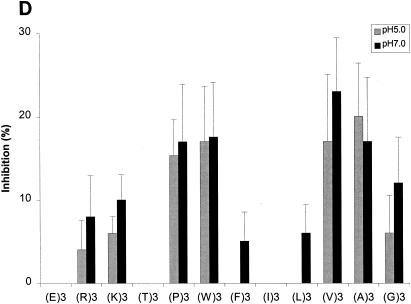
FIG. 5.
Effects of amino acyl side chains on peptide binding. (A) Representative dose-response graph of peptide inhibition of binding of phage A1-10 to OppA-1. Data points represent the mean of a minimum of three experiments performed in duplicate; error bars represent standard errors of the means. (B to D) Abilities of a panel of 12 peptides [e.g., (E)3, which represents EEE] with various characteristics in their amino acyl side chains to compete for binding to OppA proteins. Assays were performed with 20 μM concentrations of peptides. Binding at both pH 5.0 and pH 7.0 was studied for OppA-1 (B) and OppA-3 (D). Only pH 5.0 was used for assays with OppA-2 (C) due to the low activity of the protein at pH 7.0. Phage A1-10, A2-8, and A3-3 were used as the competitive ligands for OppA-1, OppA-2, and OppA-3, respectively. Experiments were performed a minimum of three times in duplicate; error bars represent standard errors of the means.