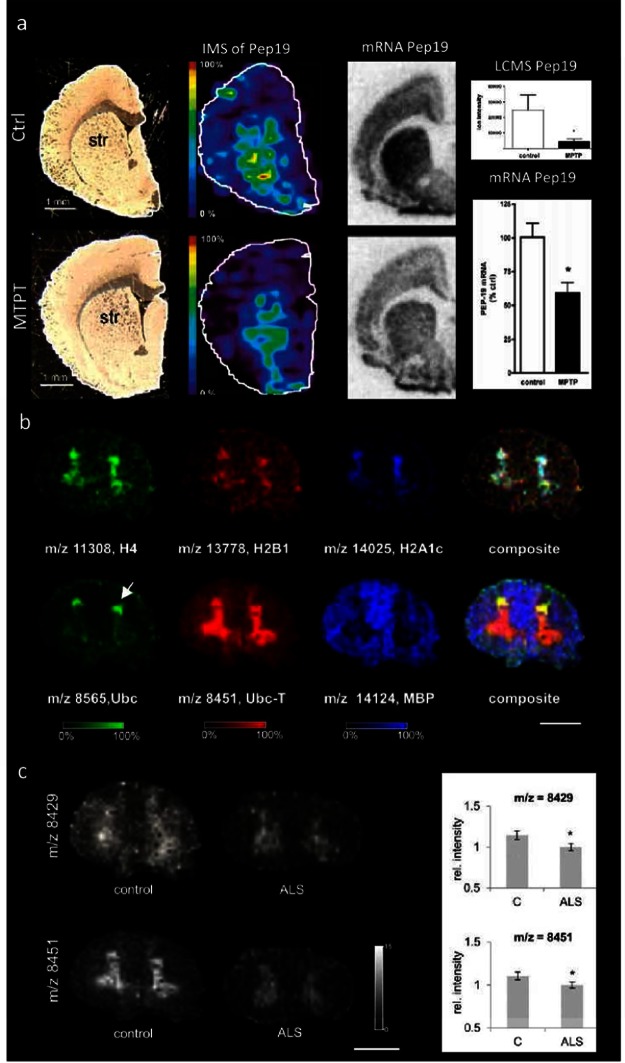
Figure 5.
Imaging mass spectrometry of proteins in neurodegenerative diseases. (a) In experimental Parkinson’s disease, MALDI IMS reveals decrease of striatal Pep19 levels in MPTP lesioned rats, as verified by in situ hybridization and LCMS in tissue extracts. (Reproduced with permission from ref (96). Copyright 2006 American Chemical Society.) (b,c) Analysis of proteins in post mortem human spinal cord using MALDI IMS. (b) Spinal cord proteins show characteristic distribution patterns that are consistent with anatomical regions, including gray (top panel) and white matter (lower panel). Here histones (H4, H2B1, H2A1c) as well as ubiquitin (Ubc) and truncated ubiquitin 1–74 (Ubc-T) were found to localize to the gray matter. In contrast, myelin basic protein shows localization to the white matter (scale bar = 1 cm). Interestingly, ubiquitin and its C-terminally truncated metabolite Ubc-T show different localizations, where Ubc is distributed to the dorsal horn (arrow) compared to Ubc-T beeing more homogeneously distributed throughout the gray matter. (c) Multivariate statistics reveal significant decreases for two protein peaks, including Ubc-T (m/z 8451) in the gray matter of ALS patients compared to controls18 (scale bar = 1 cm).