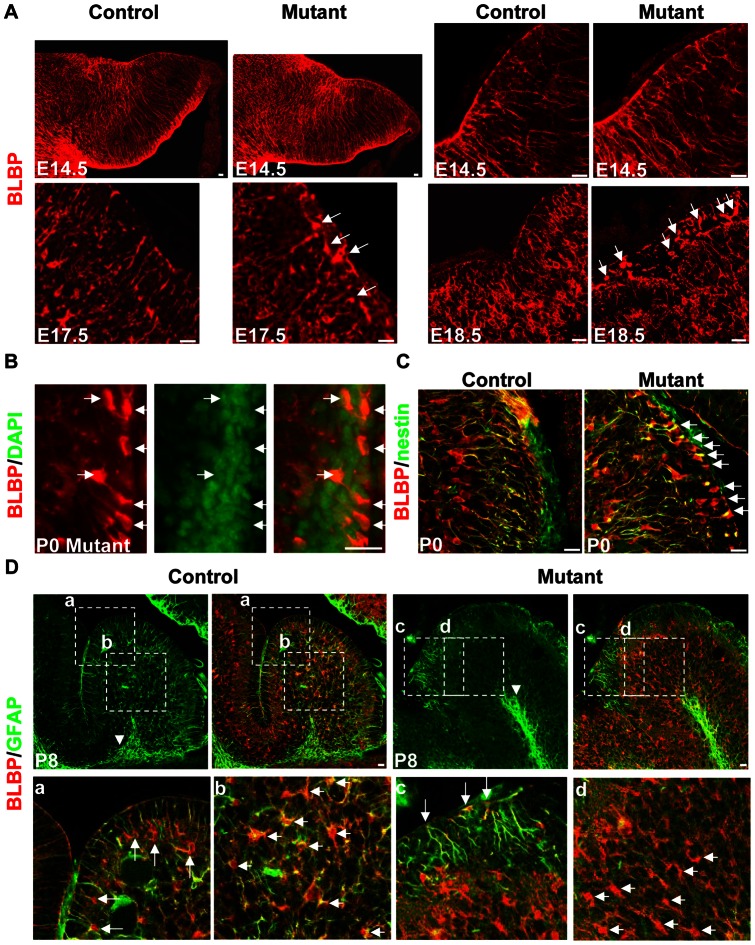
Figure 6. Developmental stage-dependent glial defects in the hGFAP-Cre, β-cateninfl/fl mouse.
(A) Sagittal sections immunolabeled with anti-BLBP antibody. At E14.5, radial glial fibers were attached to the pial surface in both control and mutant mice. The right panels were acquired under high power (60×). At E17.5, in the caudal part of the mutant cerebellum, the density of radial fibers decreased, and some BLBP-positive cell bodies appeared in the EGL (arrows). At E18.5, more ectopic glial cells were seen in the EGL (arrows). (B) Section of a P0 mutant cerebellum stained with anti-BLBP antibody and DAPI. Colocalization indicates they were indeed cell bodies (arrows). (C) Sections from P0 control and mutant mice stained with antibodies against BLBP and nestin. Many double-positive cells were found in the mutant EGL (arrows), with a polarized appearance. (D) Sections of P8 control or mutant cerebellum double-stained with anti-BLBP and anti-GFAP antibodies. In the control mouse, GFAP was expressed in the white matter glia (arrowhead in the upper panel), Bergmann glia (arrows in a) and glia in-between (short arrows in b). In the mutant mouse, GFAP was only expressed by white matter glia (arrowhead in the upper panel) and ectopic glia in the EGL (arrows in c), but not by glial cells in-between (short arrows in d). The lower panels are enlargements of the squares in the upper panels (a–d). Scale bars: 20 μm.