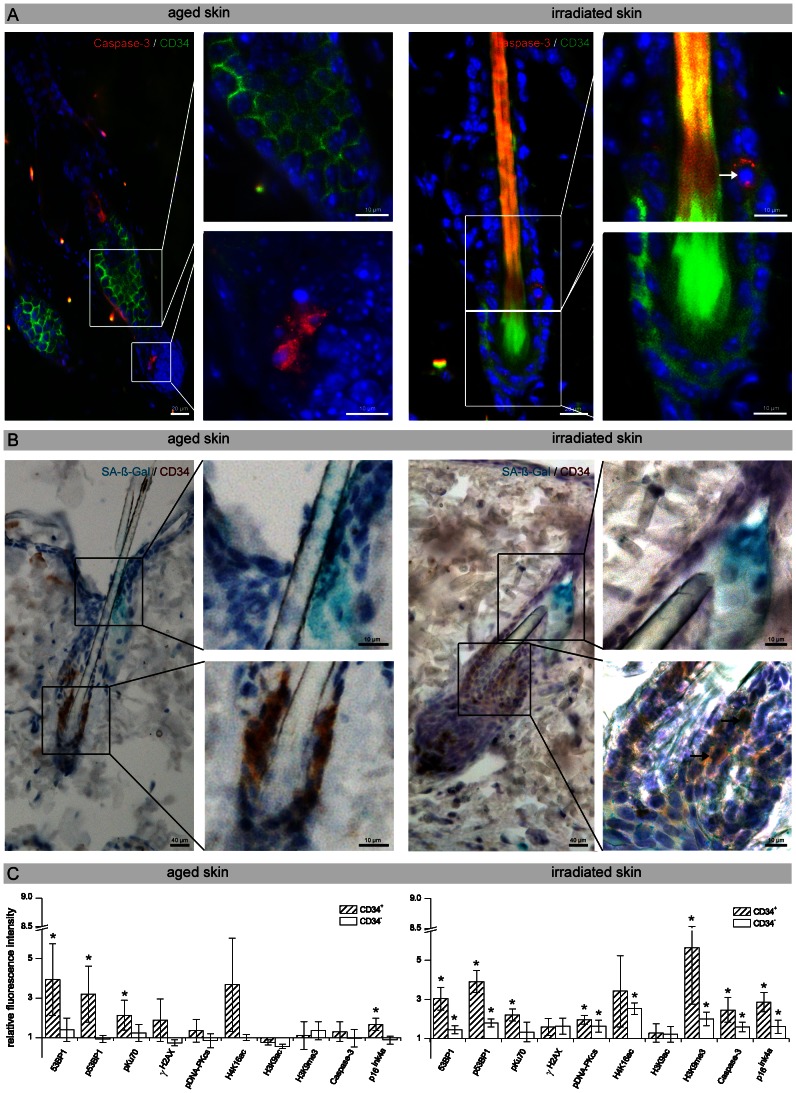
Figure 6. Biological outcome of HFSCs in aged and irradiated skin.
(A) IFM micrographs of Caspase-3 staining of skin sections derived from aged (24-months-old) and low-dose irradiated animals (40× 10 mGy). Aged skin revealed slightly increased levels of apoptotic cells (red), but not in the CD34+ HFSCs (green) of the bulge region. After protracted low-dose radiation, slightly higher levels of apoptotic cells were observed, and even some CD34+ HFSCs undergo apoptosis (arrow in the enlarged image). (B) Micrographs of the histochemical detection of SA-β-gal activity in skin sections derived from aged (24-months-old) and low-dose irradiated animals (40× 10 mGy). SA-β-gal staining of aged skin revealed an increase of the blue-dyed precipitate in the upper isthmus and infundibulum of the hair follicle, but not in CD34+ HFSCs of the bulge region (brown). In irradiated skin, some CD34+ HFSCs stained positive for SA-β-gal (two arrows in the enlarged lower image). Sporadic staining of the lumen of sebaceous ducts was also seen (enlarged upper image). (C) Analysis of the DNA damage response by flow-assisted cytometry. Relative fluorescence intensity of repair proteins, histone modifications, apoptosis and senescence markers in CD34+ and CD34– cells derived from aged (24-month-old) and irradiated (40× 10 mGy; 72 h) skin normalized to unirradiated young skin (3-month-old). Data are presented as means from three different experiments ±SE. * significant difference compared with unirradiated young skin.