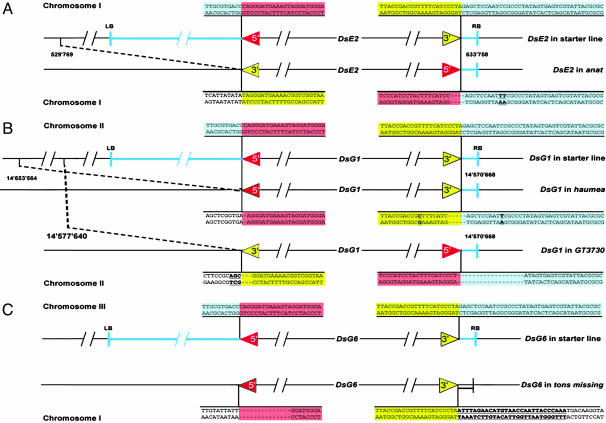
Fig. 4.
Comparison of Ds junctions in the starter lines and after transposition in the mutants ana, hma, GT3730, and tms. Schematic representation of the Ds element in the starter lines DsE2 (A), DsG1 (B), and DsG6 (C) and in the corresponding mutant. Black line, plant genomic sequence; blue line and highlighted, T-DNA fragment and sequence junction; red and yellow arrows and highlighted sequence, 5′ and 3′ Ds end, respectively. In ana (A), DsE2 retention is accompanied by a 3-bp deletion at the Ds5′ terminus, a 1-bp deletion of the T-DNA vector at the site of excision, and a 104-kb genomic deletion flanking the 3′ end of Ds. At position +11 bp counted from the Ds3′ end, an additional T was inserted, and a C→T exchange occurred (bold and underlined). In hma (B), DsG1 is excised and reinserted in the same orientation at the site of excision causing an 83-kb genomic deletion. On the Ds5′ terminus, a single base pair is deleted, whereas the four outermost bases on the Ds3′ end are missing. Aberrant transposition is accompanied with single base exchanges at position -12 (T→C) and at position + 11 (C→T), as referenced to the 5′ terminus (bold and underlined). In GT3730 DsG1 reinserted at the site of excision in opposite orientation accompanied by a 7-kb genomic deletion at the 3′ flank and a 17-bp deletion at the 5′ flank of the mutant Ds where the 3-bp GAT are substituted by CGA. In tms (C), 14 bp on the Ds5′ terminus are deleted, and 28-bp repetitive sequences from an AtREP3 annotated transposon (underlined and bold) flank the Ds3′ terminus.