Fig. 1.
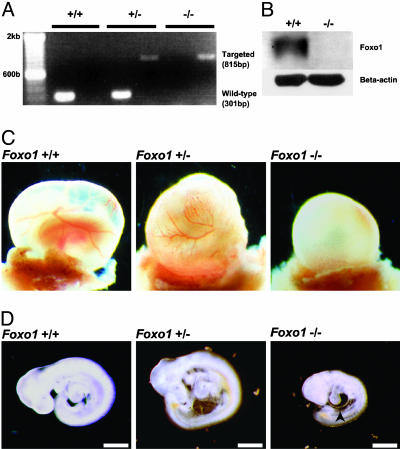
Disruption of the Foxo1 gene results in embryonic lethality. (A) PCR analysis with genomic DNA from E9.5 yolk sacs obtained from a mating of Foxo1+/- mice. PCR amplification from the wild-type and Foxo1-targeted loci resulted in fragment sizes of 301 bp and 815 bp, respectively. Samples were independently amplified with each primer set. (B) Western blot analysis of lysates from E9.5 Foxo1+/+ and Foxo1-/- embryos by using antibodies against Foxo1 and β-actin. (C) At E9.5, both Foxo1+/+ and Foxo1+/- yolk sacs had well developed blood vessels, whereas Foxo1-/- yolk sacs lacked them. (D) At E9.5, Foxo1+/+ and Foxo1+/- embryos were phenotypically indistinguishable in appearance, whereas Foxo1-/- embryos were approximately half their size. In addition, cardiac looping was retarded and the pericardium was distended (arrowhead). (Scale bar, 500 μm.)