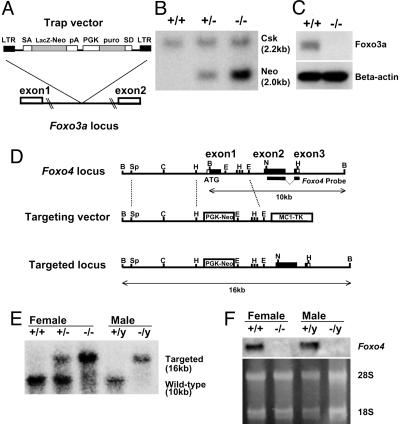
Fig. 4.
Targeted disruption of the Foxo3a gene and Foxo4 gene. (A) Targeting strategy for Foxo3a. A retroviral promoter trap vector was inserted in intron 1 of Foxo3a. SA, splice acceptor site; SD, splice donor site; LTR, long terminal repeat sequence; pA, polyadenylation signal; puro, puromycin. (B) Southern analysis of SacI-digested genomic DNA obtained from a mating of Foxo3a+/- mice by using the Neo- and Csk-specific probes. Different intensities demonstrated by hybridization of the Neo-specific probe discriminate zero, one, or two Foxo3a gene disruptions, representing +/+, +/-, and -/- mice, respectively. (C) Western analysis of lung tissue lysates from Foxo3a+/+ and Foxo3a-/- mice by using antibodies against Foxo3a and β-actin. (D) Restriction maps of the wild-type Foxo4 locus, the targeting vector, and the targeted locus. The targeting vector contained a PGK-Neo cassette instead of the Foxo4 exon1. A targeting probe (3′ region of Foxo4 cDNA) was also indicated. Restriction enzymes were indicated as B, BamHI; C, ClaI; E, EcoRI; H, HindIII; N, NcoI; and Sp, SpeI. (E) Southern analysis of BamHI-digested genomic DNA obtained from Foxo4 female (+/+, +/-, and -/-) and male (+/y and -/y) mice by using a probe from the 3′ region of Foxo4 cDNA. The Foxo4 wild-type allele (10 kb) and targeted allele (16 kb) were indicated. (F) Northern analysis of total RNA from skeletal muscle of Foxo4 female (+/+ and -/-) and male (+/y and -/y) mice by using the same probe used for Southern blot analysis. The ethidium bromide-staining 28S and 18S bands are also indicated.