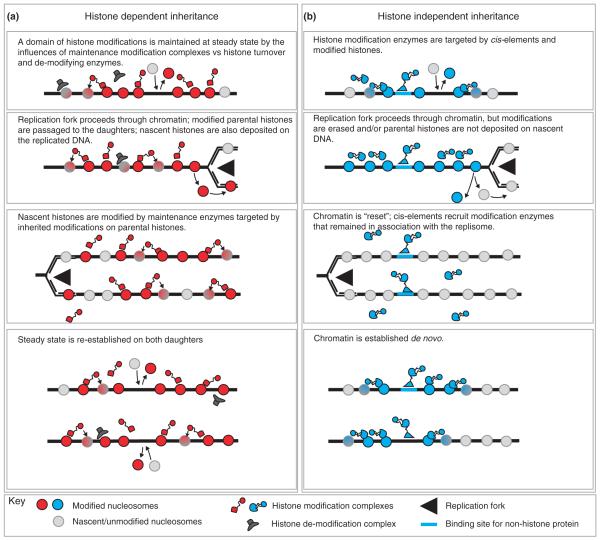
Figure 1.
Simplified schematic depiction of mechanisms by which chromatin domains may be maintained through DNA replication. (a) Histone-dependent inheritance: parental histones and modifications are retained on the daughter genomes following replication fork passage, but are diluted by nascent histones. Inheritance of modifications is mediated by maintenance enzymes targeted to inherited modifications. (b) Histone-independent inheritance: parental histones or modifications are not maintained; the chromatin state is re-established de novo by factors targeted to cis-acting elements in the DNA.