Fig. 6.
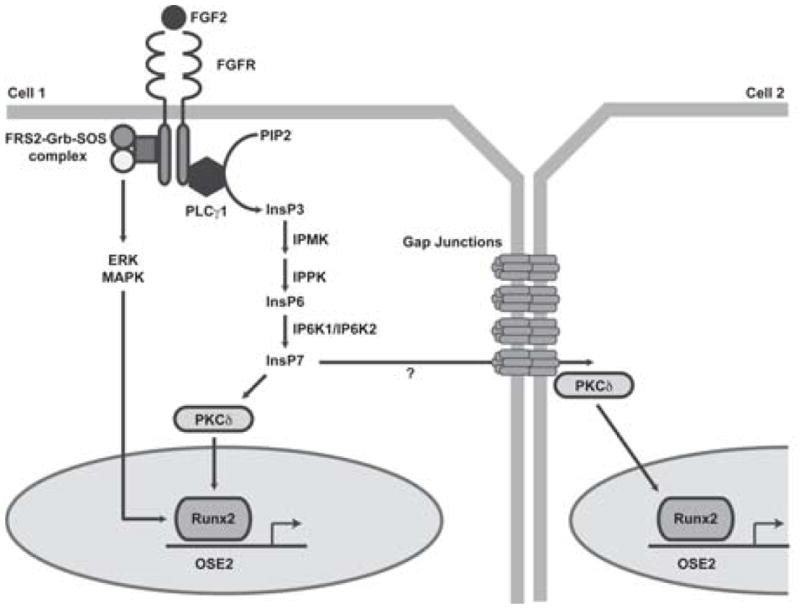
Model of Cx43 potentiated Runx2 activity via an inositol pyrophosphate second messenger following FGF2 stimulation. Upon binding to its receptor (FGFR) in one cell, FGF2 activates PLCγ1, generating DAG and InsP3 (IP3). Subsequently, the activity of IPMK and IP6K1 leads to the production of inositol polyphosphates and pyrophosphates, such as InsP6 (IP6) and InsP7 (IP7). The InsPs activate PKCδ, which translocates to the nucleus where it interacts with Runx2, increasing its transcriptional activity and driving the expression of osteoblast genes. In addition, we speculate that these small, water soluble second messengers may be communicated to adjacent cells via Cx43 containing gap junctions. In the coupled cell, PKCδ, which is locally recruited to the Cx43-containing gap junction channel, can re-initiate signaling in this cell, independent of direct stimulation by FGF2, resulting in a potentiation of the response among coupled cells.
