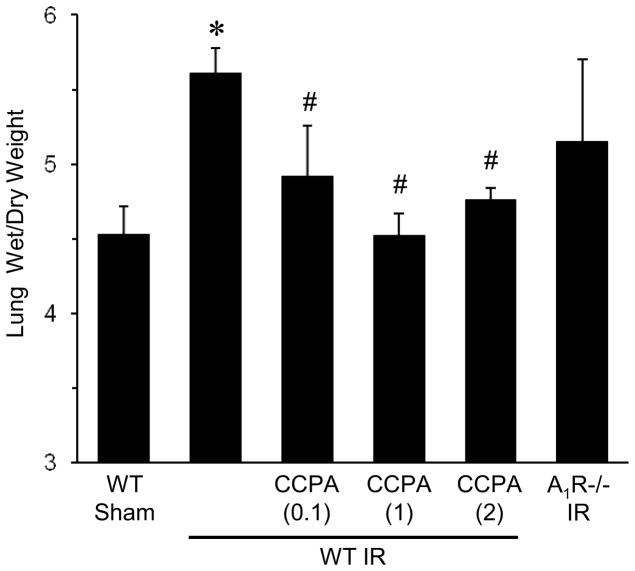
Figure 2. Pulmonary edema after IR is significantly reduced by CCPA.
Lung wet/dry weight ratio was measured after IR or sham surgery in A1R−/− mice and in WT mice treated with vehicle or CCPA (doses in mg/kg are shown in parentheses) prior to ischemia. Lung wet/dry weight was significantly increased after IR in WT mice, which was significantly attenuated by CCPA treatment. Lung wet/dry weight after IR was also elevated in A1R−/− mice after IR similar to WT mice after IR. Lung wet/dry weight was similar between WT and A1R−/− mice after sham surgery (data not shown). *P < 0.05 vs. WT sham, #P < 0.05 vs. WT IR. Means ± SD are shown.