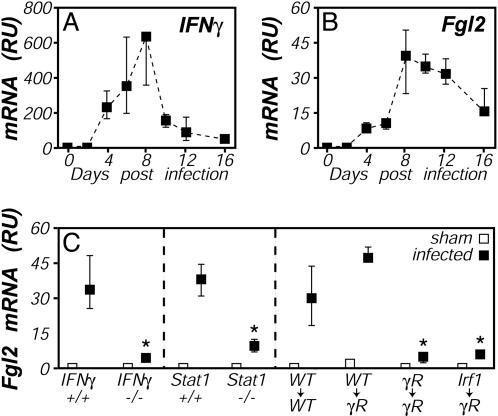
Fig. 2.
IFNγ-, Stat1-, and Irf-dependent up-regulation of Fgl2 expression during T. gondii infection. (A and B) Mice were perorally infected with 10 ME49 T. gondii cysts, and tissues were harvested on the indicated days. Relative levels of mRNA encoding IFNγ (A) and Fgl2 (B) were determined by real-time PCR. (C) Mice were infected with T. gondii (filled symbols) or were sham-infected (open symbols). Tissues were harvested on day 8 after infection, and relative levels of Fgl2 mRNA were determined by real-time PCR. (Right) Shown is an experiment using bone marrow chimeras in which WT, IFNγR-deficient, or Irf1-deficient bone marrow was used to reconstitute lethally irradiated WT or IFNγR-deficient hosts. Throughout, data depict the median and range of four to five mice per time point. *, P < 0.05.