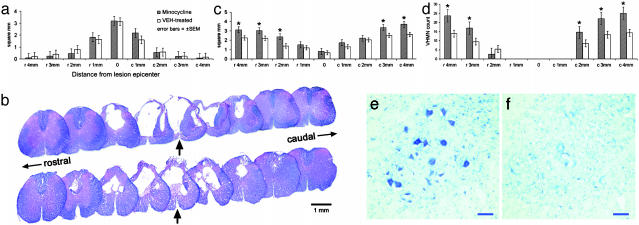
Fig. 3.
(a) Lack of significant effect of minocycline (total dose of 495 mg/kg per rat over 5 days) on lesion volume at the injury epicenter and adjacent tissue up to 4 mm rostral and caudal to the epicenter, in 1-mm increments (solvent blue and hematoxylin/eosin staining). (b) Representative transverse spinal cord sections after T10 contusion injury at the epicenter and in 1-mm increments rostral and caudal to the epicenter in a rat receiving minocycline (Upper) and saline vehicle (Lower). Epicenter sections are marked by arrows. (c) Overall significant difference (P = 0.014, repeated-measures ANOVA) between rats receiving minocycline or saline vehicle (n = 10 rats per group) in the average area of residual total white matter (i.e., white matter and hypomyelinated white matter; solvent blue and hematoxylin/eosin staining) (24), as well as 2, 3, and 4 mm rostral and 3 and 4 mm caudal to the lesion epicenter (P < 0.03, unpaired Student's t test). (d) Minocycline treatment significantly protected ventral horn neurons 3 and 4 mm rostral to the epicenter (P < 0.03, repeated-measures ANOVA), as well as 2, 3, and 4 mm caudal to the epicenter (P < 0.05, unpaired Student's t tests). (e and f) Representative transverse cresyl violet-stained sections 2 mm caudal to the injury epicenter in a rat receiving minocycline (e) or saline vehicle (f). (Scale bar = 50 μm.)