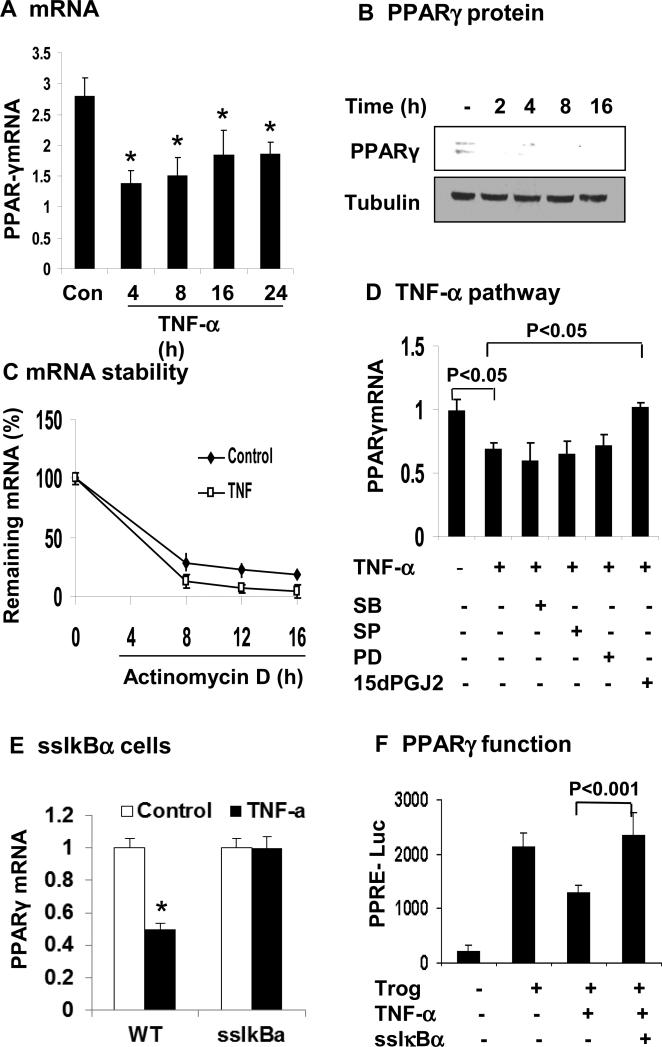
Figure 5. TNF-α inhibits PPARγ expression through NF-κB pathway.
(A) Inhibition of PPARγ mRNA expression by TNF-α in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. The cells were serum-starved overnight and treated with TNF-α (20 ng/ml) for hours as indicated. PPARγ mRNA was determined in qRT-PCR. (B) Inhibition of PPARγ protein expression by TNF-α. PPARγ protein was determined in the whole cell lysate in a Western blot. (C) PPARγ mRNA stability. De novo mRNA transcription was inhibited by the addition of actinomycin D (5 μg/ml). The residual mRNA of PPARγ was quantified by qRT-PCR. Values represent percentage of residual mRNA versus mRNA level at time 0. (D) Blocking of TNF-α activity by the NF-κB inhibitor. The 3T3-L1 adipocytes were pretreated with the pharmacological inhibitors for 30 min before addition of TNF-α. The inhibitors are SB203580 (SB, 10 μM), SP600125 (SP, 25 μM), PD98059 (PD, 40 μM), and 15dPGJ2 (15 μM). mRNA was determined in the cells after 16 h. (E) PPARγ mRNA was quantified in ssIκBα 3T3-L1 adipocytes after TNF-α treatment. (F) The transcriptional activity of PPARγ was analyzed in 3T3-L1 fibroblasts using the PPRE (3X)-luciferase reporter system in the transient transfection. Expression vector of ssIκBα was co-transfected to block NF-κB activation. At 24 h after transfection, the cells were serum-starved overnight and treated with troglitazone (10 μM) and TNF-α (20 ng/ml). In this figure, each bar represents mean ± SEM (n=3). *, P< 0.05.