Figure 1.
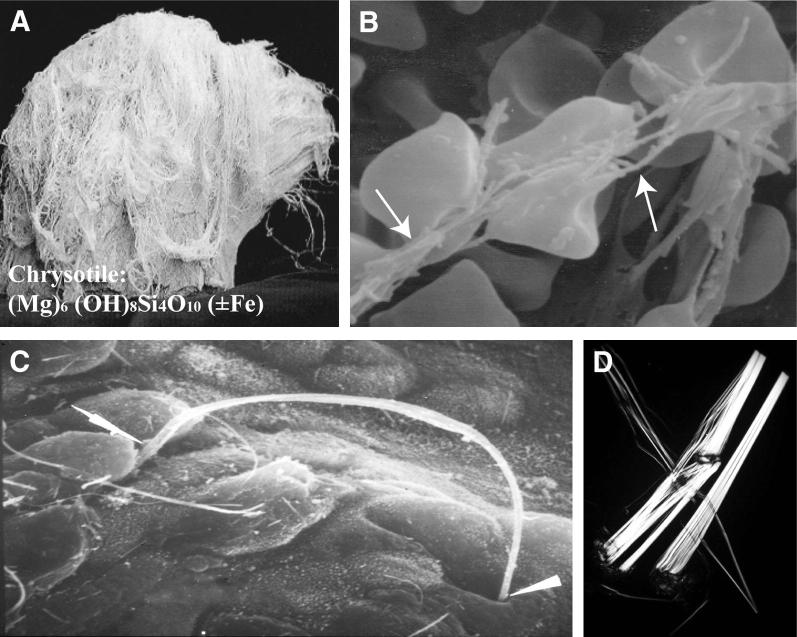
Properties of chrysotile (white) asbestos. A: Image of bundle of curly chrysotile fibers before processing. B: Scanning electron micrograph of chrysotile fibers (arrows) causing deformation of red blood cells. Chrysotile is positively charged, hemolytic, and cytolytic, primarily due to its magnesium content. Leaching of magnesium renders chrysotile less toxic and also results in chrysotile fiber dissolution over time. C: Scanning electron micrograph of interaction of long chrysotile fiber with the respiratory epithelium of the alveolar duct junction after inhalation by rats. Arrowheads show points of contact with and between epithelial cells. Subsequent penetration into and between cells leads to fiber deposition in the lung interstitum and access to the visceral pleura and pleural space. D: Polarized microscopy showing chrysotile fibers and fibrils.
Photomicrograph is a courtesy of Lee Poye (J3 Resources, Inc., Houston, TX) Original magnification, ×100.