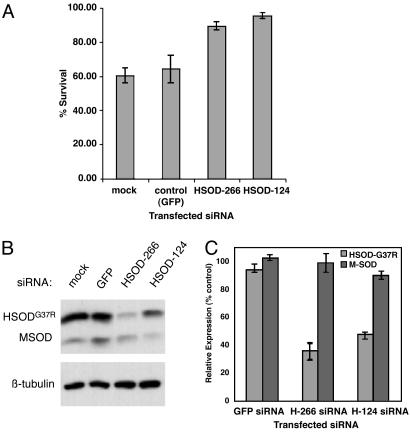
Fig. 4.
Selective silencing of mutant HSOD1G37R rescues CsA-induced cell death. (A) Quantitative analysis of cell survival in siRNA-transfected SOD1G37R N2a cells treated with 7 μg/ml CsA. Cells were transfected with control (GFP) siRNA or SOD1 siRNAs H-266 or H-124, or exposed to transfection reagent but no siRNA (mock). Viable cells were estimated by using the WST-1 assay (see Materials and Methods); survival is expressed as the ratio of CsA-treated to untreated cells within each transfection experiment. Data represent the survival mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. (B) Representative immunoblot showing relative levels of mutant human (HSOD1G37R; Upper, upper band) and endogenous wild-type mouse SOD1 (MSOD; Upper, lower band) in samples from A. Proteins were extracted from untreated (no CsA) cells at the conclusion of the survival assay. Lower shows β-tubulin as loading control. (C) Quantification of HSOD1G37R and MSOD1 levels from immunoblots as in B from two independent experiments. SOD1 protein levels are expressed as percentage of control (mock-transfected) normalized to tubulin. Error bars represent standard deviation.