Table 1.
In vitro HDAC inhibition activity of novel HDAC-Topo I inhibitors.
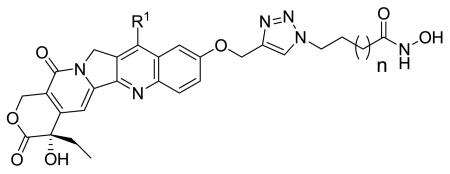
| Compound | n | R1 | HeLaa IC50 (nM) |
HDAC 1b IC50 (nM) |
HDAC 6b IC50 (nM) |
HDAC 8b IC50 (nM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5a | 1 | -CH2CH3 | N.D. | N.D. | 85 ± 34 | 1726 ± 577 |
| 5b | 2 | -CH2CH3 | 155.4 | NT | NT | NT |
| 5c | 3 | -CH2CH3 | 120.7 | 129 ± 33 | 42 ± 6 | N.D. |
| 5d | 4 | -CH2CH3 | 64.65 | 50 ± 7 | 36 ± 5 | N.D. |
| 5e | 5 | -CH2CH3 | 212.3 | 369 ± 111 | 75 ± 34 | 2599 ± 475 |
| 5f | 2 | -H | 144.5 | 116 ± 40 | 260 ± 40 | N.D. |
| 5g | 3 | -H | 112.2 | N.T. | N.T. | N.T. |
| 5h | 4 | -H | 56.2 | 37 ± 7 | 81 ± 26 | 1046 ± 316 |
| SN-38 | - | - | N.D. | N.T. | N.T. | N.T. |
| SAHA | - | - | 65.0 | 38 ± 2 | 27 ± 2 | 1989 ± 156 |
N.D. – Nondeterminable within tested range, 1 nM – 10 μM; N. T – Not tested.
HeLa nuclear extract. Each value is obtained from three independent experiments.
Data obtained through contract arrangement with BPS Bioscience (San Diego, USA; www.bpsbioscience.com). Assays were performed in duplicates at each concentration and data reported with standard error.29, 34c
