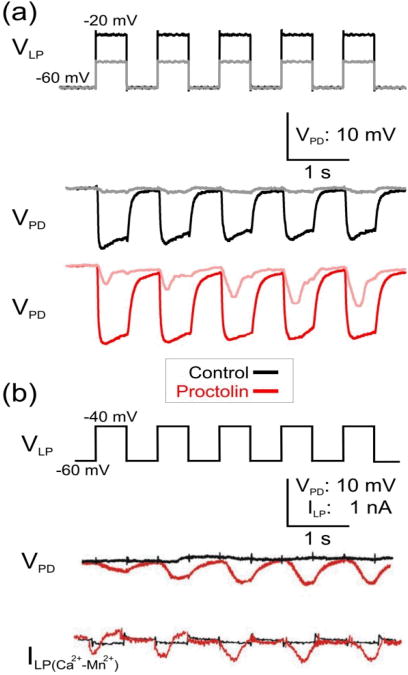
Figure 1. Proctolin modulates the short-term dynamics of the LP to PD inhibitory synapse in response to presynaptic depolarization pulses of different amplitude.
(a) LP neuron was voltage-clamped at -60 mV and stimulated with a series of five square pulses of 40 mV (VLP: black trace) or 20 mV (VLP: gray trace) amplitudes in control saline and in 10−6 M proctolin and the synaptic potentials were recorded in the PD neuron. In control saline the LP to PD synapse was depressing. In proctolin, in response to 20 mV presynaptic pulses, the synapse showed facilitation (pink) but it remained depressing (red) in response to the 40 mV pulses. (b) The proctolin-induced facilitation of the LP to PD synapse in response to low amplitude 20 mV presynaptic pulses is associated with the activation of Ca2+-like inward current ΔILP=ILP(Ca2+)−ILP(Mn2+) (Zhao et al. 2011). The amplitude of the current ΔILP exhibits no change in control (black) and increases in proctolin (red) with each pulse.