Fig. 4.
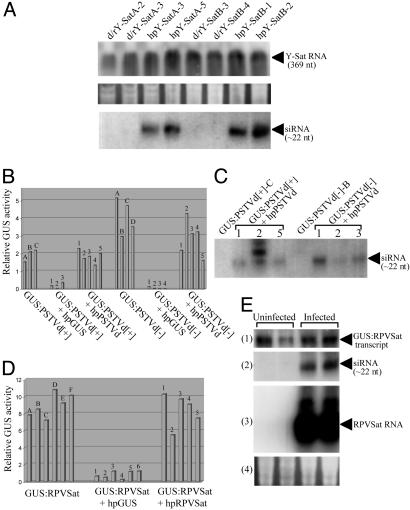
(A) Replicating Y-Sat RNA is resistant to hpRNA-induced RNA silencing. (Top) Northern blot hybridization analysis of (+) strand Y-Sat RNA in Y-Sat-infected d/rY-Sat or hpY-Sat tobacco. Total RNA (20 μg) isolated from leaf tissue collected from a pool of approximately two to five Y-Sat-infected T1 plants of each line was hybridized with antisense Y-Sat RNA probe. (Bottom) Detection of Y-Sat siRNA in uninfected d/rY-Sat or hpY-Sat tobacco. High-molecular weight RNA was removed from 120 μg of total RNA (isolated from a pool of several uninfected T1 plants of each line) by precipitation with 5% polyethylenglycol 8000 and 0.5 M NaCl, and the small RNAs were pelleted from the supernatant with 0.3 M NaOAc and 3 volumes of ethanol and used for the analysis. Hybridization was performed by using full-length antisense Y-Sat RNA as probe. (Middle) RNA loading control for Top. (B-E) Nonreplicating subviral RNA sequences are also resistant to RNA silencing. (B and D) Relative GUS activity of 5 μg of protein from tobacco transformed with GUS:PSTVd[+], GUS:PSTVd[-], or GUS:RPVSat or their supertransformants with hpGUS, hpPSTVd or hpRPVSat. The uppercase letter above each bar represents plants regenerated from the same primary transformant (for GUS:PSTVd[+] and GUS:PSTVd[+]) or T1 plant (for GUS:RPVSat), and the number above each bar indicates an independent supertransformant. (C) Detection of siRNA from a subset of plants in B by Northern blot hybridization using full-length sense PSTVd RNA as probe. (E) Northern blot hybridization analysis of duplicate GUS:RPVSat regenerants uninfected or infected with potato leaf roll virus that is required to support RPVSat replication. The blots, from 1 to 4, show total RNA hybridized with antisense GUS RNA (11); siRNA hybridized with antisense RPVSat sequence (11); total RNA hybridized with antisense RPVSat RNA, where the strong signals indicate the presence of replicating RPVSat RNA; and RNA loading control for blots 1 and 3.