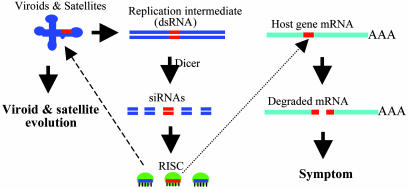
Fig. 5.
A model for the role of RNA silencing in the pathogenicity and evolution of viroids and viral satellite. Replication of the subviral RNAs generates dsRNA intermediates, which are processed by Dicer into 21- to 25-nt siRNAs, and these siRNAs are then incorporated into siRNA-ribonuclease complexes (RISC). If significant sequence identity exists between a region in the subviral RNA genome and a region in host gene mRNA (shown in red), RISC will target the host gene for degradation leading to symptom development. RISC can also target the subviral genome for degradation, forcing the subviral RNA to evolve and to adopt and maintain RNA silencing-resistant secondary structure.