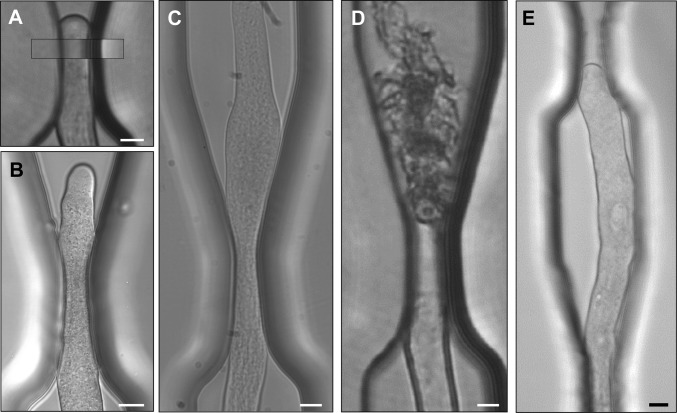
Fig. 2.
Different types of pollen tube behavior during passage through a microgap. (A) The pollen tube deflects the sidewalls almost completely to maintain its diameter. (Inset) Same position of the undeformed microgap before the invasion of the pollen tube. (B) The pollen tube becomes narrower in the y-direction to pass the gap and widens to the original diameter after passage. (C) The pollen tube becomes wider than the original tube after passing the gap, but eventually returns to the original diameter. (D) Following passage through the gap, the pollen tube bursts. (E) The pollen tube stalls and cannot pass through the gap. The buckling indicates that a force is exerted against the wall of the gap. Bars: 10 µm (bar in A applies to A–D).