Figure 6.
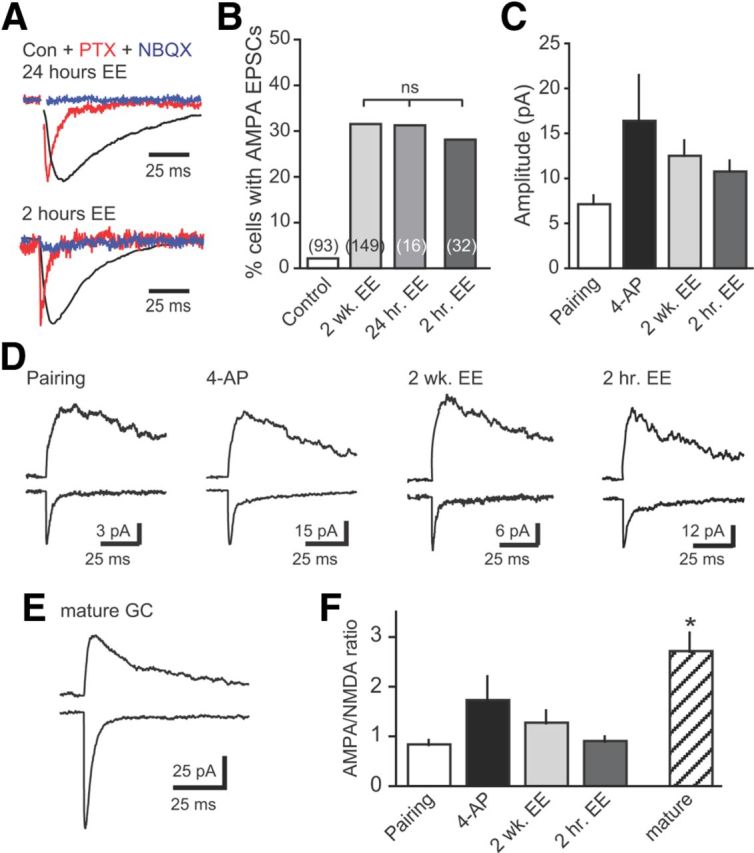
Short exposure to EE is sufficient for unsilencing in vivo. A, Examples of synaptic currents in newborn GCs after 24 or 2 h of EE, demonstrating that a short exposure to EE is sufficient for synapse unsilencing. EPSCs insensitive to PTX (red; normalized to peak of GPSC) were blocked by NBQX (5 μm; blue). B, Summary of the percentage of newborn GCs with AMPA EPSCs after exposure to EE for 2 weeks (data from Fig. 5), 24 h, or 2 h. C, The amplitude of AMPA EPSCs induced by pairing, 4-AP-driven synaptic activity, and EE was similar (p = 0.22, one-way ANOVA). D, Examples of AMPAR and NMDAR EPSCs in newborn GCs, measured at −70 mV and at +40 mV, respectively. E, Example of AMPAR and NMDAR EPSCs in a neighboring mature GC. F, The AMPA/NMDA ratio was similar in newborn GCs across all conditions (p = 0.16, ANOVA) but lower than in mature GCs (n = 15; *p < 0.01, t test of all newborn GCs compared with mature GCs). Con, Control.
