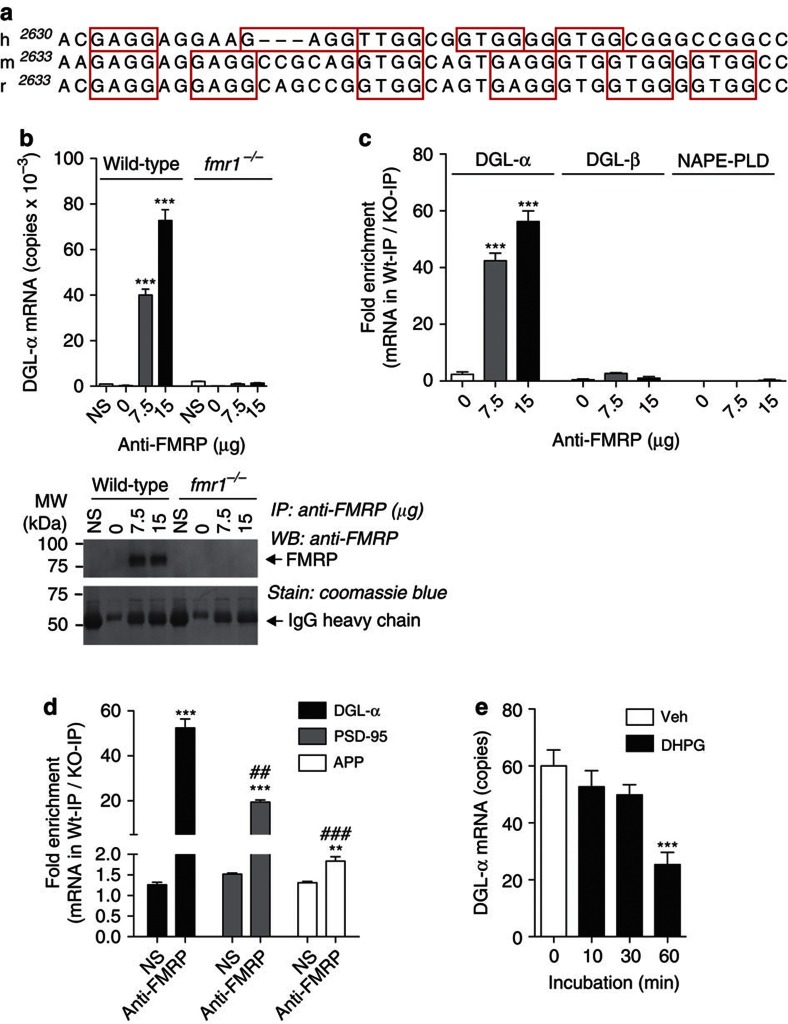
Figure 1. DGL-α mRNA binds to FMRP.
(a) Alignment of the coding region in human (h), mouse (m) and rat (r). DGL-α mRNAs reveal a putative G-quartet sequence within a G-rich region containing several DWGG repeats. The canonical G-quartet motif is DWGG-N(0–5)-DWGG-N(0–3)-DWGG-N(0–2)-DWGG, where D is any nucleotide except C, and W is A or U. The DWGG repeats are boxed in red. (b) Co-immunoprecipitation of FMRP with DGL-α mRNA. Brains from wild-type or fmr1−/− mice were homogenized and centrifuged at 70,000 g for 30 min. The supernatant (1 mg protein) was incubated with the indicated amounts of anti-FMRP antibody or normal serum (NS), and the immunocomplex was precipitated using protein G-sepharose beads. Top, levels of DGL-α mRNA in the immunoprecipitates were quantified by real-time quantitative PCR (n=3, ***P<0.001). Bottom, a portion of the immunoprecipitate was subjected to SDS–PAGE and western blot analyses to confirm the presence of FMRP. (c,d) Analyses of mRNAs encoding for DGL-α, DGL-β and NAPE-PLD (c) or positive control PSD-95 and amyloid precursor protein (d) in anti-FMRP-immunoprecipitates (n=3, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 compared with NS, ##P<0.01 and ###P<0.001 compared with DGL-α-anti-FMRP). Similar results were obtained using fmr1−/− mice bred on either a FVB.129 background (b,c) or a C57BL/6J background (d). (e) DHPG-induced dissociation of DGL-α mRNA from FMRP in cultured cortical neurons. Rat primary neurons were prepared from embryonic day 18 cortex, as described55. Cells were treated with DHPG (100 μM) in culture medium and harvested at the indicated time. Levels of FMRP-bound DGL-α mRNA were determined by anti-FMRP immunoprecipitation and quantitative PCR, as described in Methods (n=5, ***P<0.001). Results are representative of at least two independent experiments. Significance was determined using two-tailed Student's t-test. Error bars represent s.e.m.