Figure 4. The γH2AX/MDC1 and H4K20me/53BP1 interactions suppress DNA end resection and promote repair of CSR-associated breaks by NHEJ.
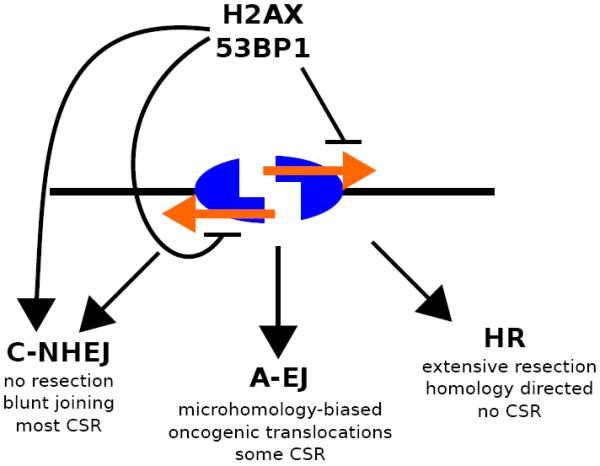
Under normal conditions, these chromatin-mediated interactions facilitate synapsis and repair of two different broken switch regions. These CSR joins mediated by the C-NHEJ pathway show little evidence of resected DSB ends and constitute the majority of successful CSR. In the absence of C-NHEJ, A-EJ mediates some level of CSR but also mediates aberrant joining in the form of chromosomal translocations. In the absence of either H2AX or 53BP1, extensive resection occurs on unrepaired DSBs, thereby inhibiting NHEJ pathways, and ultimately leading to repair of the DSB by HR without class-switching. Orange arrows indicate 5' to 3' DNA end resection of a DSB incurred within an Igh switch region.
