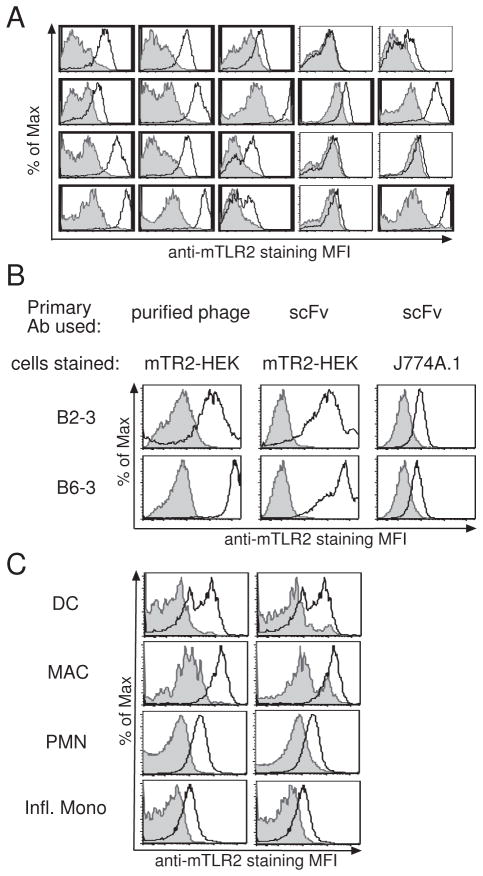
Figure 1. Identification and characterization of anti-mTLR2 antibody clones.
(A) Screening anti-mTLR2 antibody clones. Raw phage preparations of individual clone were used to stain mTLR2-HEK (white) or YFP-HEK (gray) cells. 20 representative clones are shown here. Positive clones are indicated in bold. (B) Validation of anti-mTLR2 binding. Purified phage (left) or corresponding scFvs (center) were used as primary Ab to stain on mTLR2-HEK cells (white) or YFP-HEK (gray). Right panel shows J774A.1 cells stained with anti-mTLR2 scFvs (white) or with anti-Tie2 scFv (gray). (C) mTLR2-scFv bind to primary mouse lung cells. Purified anti-mTLR2 scFv was used as primary Ab to stain mouse lung cells (white). In the left panel, anti-Tie2 antibody was used as a negative control antibody (gray). In the right panel, cells harvested from a mTLR2 konck-out mouse were used as negative control cells (gray). Lungs were harvested from intranasally LPS-treated mouse and myeloid cells populations were identified as described by Lin et al.