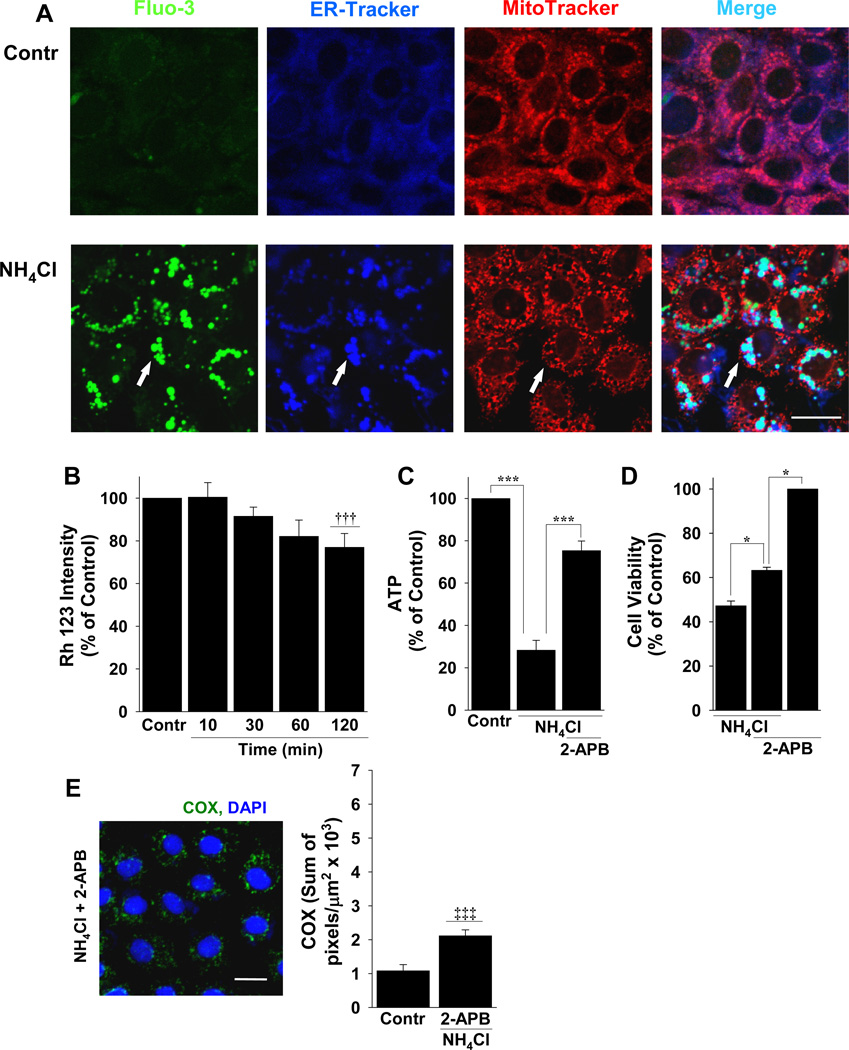
Figure 4.
A/A-induced NMDA-mediated Ca2+ localizes to ER and is transferred to mitochondria, causing mitochondrial damage and cell death. (A) Untreated (live) RGM1 cells (Contr) or cells treated with A/A (NH4Cl) were incubated simultaneously with Fluo-3 (green), ER-Tracker (blue), and MitoTracker (red) and the merged images (turquoise) were used to examine the co-localization of fluo-3 with the ER or mitochondria. 2-APB, was used to block the transfer of Ca2+ from ER to mitochondria and the resulting effect this had on (B) mitochondrial membrane potential with Rh 123, (C) ATP production, (D) cell viability, and (E) mitochondrial membrane damage by staining with anti-COX (green). n ≥ 3; * P < 0.05 and *** P < 0.001; comparisons as indicated by brackets; ††† P < 0.001 compared to A/A alone in Fig. 3A; ‡‡‡ P < 0.001 compared to A/A in Fig. 3C; scale bars, 20 µm.