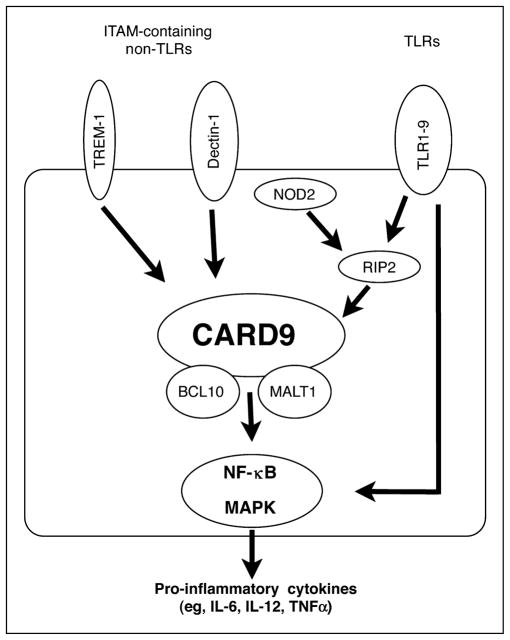
Figure 2. CARD9 functions in myeloid cells.
After activation of membrane-bound microbial sensors such as Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM)-containing non-TLRs, and the cytoplasmic sensor NOD2 (CARD15), signaling pathways converge on CARD9. Stimulation of dectin-1 with the fungus-derived ligand zymosan or of TREM-1 (unknown specific ligand) induces phosphorylation of specific tyrosine residues in the ITAMs, leading to downstream formation of a signaling complex of CARD9 with other adaptor proteins, particularly BCL10 and MALT1. TLRs can activate RIP2 (CARD3) and CARD9 in response to a broad range of microbial ligands, while NOD2 interacts with RIP2 and CARD9 via CARD–CARD interactions upon intracellular recognition of muramyl dipeptide. Formation of the signaling complex with CARD9, BCL-10 and MALT1 leads to activation of nuclear factor (NF)-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK), and subsequently secretion of proinflammatory cytokines. TLRs can also activate NF-κB through a CARD9-independent pathway.