Figure 3.
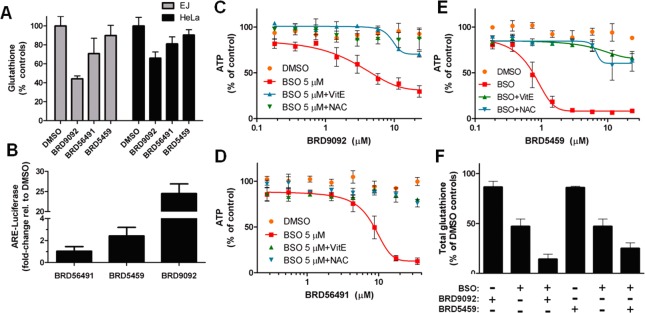
Cellular effects of ROS-enhancing, nontoxic compounds. (A) Total cellular glutathione after treatment with the indicated compounds (BRD9092, 23.2 μM; BRD56491, 35 μM; BRD5459, 11.7 μM) was measured in EJ and HeLa cells. (B) BRD9092 and BRD5459, but not BRD56491, elevate antioxidant response element (ARE) promoter transcription in a luciferase-based reporter-gene assay in IMR-32 cells. Data are expressed as mean ± SD, n = 3 (ARE reporter assay, n = 4). (C–E) Three ROS-enhancing nontoxic compounds were tested for viability in the presence of a nontoxic dose (5 μM) of BSO (a glutathione synthesis inhibitor), 200 μM vitamin E, or 5 mM N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) in EJ cells. ATP values were calculated relative to control wells lacking the indicated BRD compound but containing BSO and antioxidant when applicable. All treatments were nontoxic individually (Supporting Figure 4). (F) Pairing of BRD5459 (2.9 μM) or BRD9092 (11.6 μM) with BSO (5 μM) leads to enhanced depletion of glutathione. All data are expressed as mean ± SD, n = 3.
