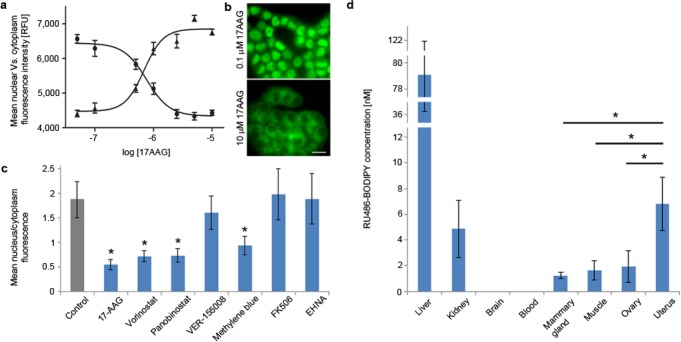
Figure 3.
Effect of PR-multiprotein-complex modulators on RU486-BODIPY mediated PR nuclear translocation. (a) Dose–response curve of PR nuclear translocation in T47D cells treated with HSP90 inhibitor 17-AAG. Cells were incubated with 17-AAG at indicated concentrations for 1 h before treated with 5 nM RU486-BODIPY. Each data point represents mean nuclear (●) or cytoplasmic (▲) fluorescence intensity of 30 cells. Error bars represent ± SD. (b) Effect of 17-AAG on PR nuclear translocation at 0.1 and 10 μM. Scale bar 20 μm. (c) Cellular distribution of 5 nM RU486-BODIPY in T47D cells pretreated with: 0.1% v/v DMSO for 12 h (control), 10 μM 17-AAG or 500 μM EHNA for 1 h, 10 μM FK506 for 2 h, 10 μM vorinostat, panobinostat, VER-155008, or methylene blue for 12 h. Each bar represents the ratio of mean nucleus-to-cytoplasm fluorescence of 30 cells. Error bars represent ± SD. * p < 0.01 (two-tail t-test). (d) Tissue distribution of RU486-BODIPY in FVB/N female mice 4 h post I.V. injection (n = 4). Error bars represent ± SD. * p < 0.05 (one-tail t-test).