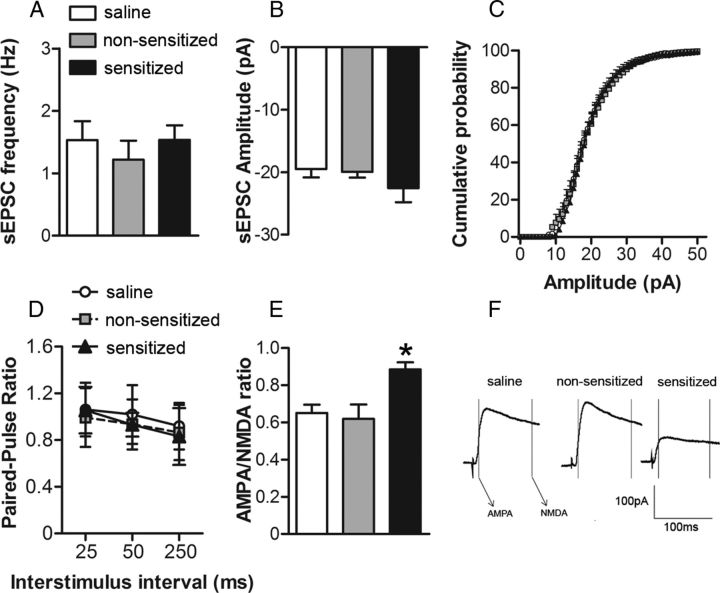
Figure 2.
The development of ethanol locomotor sensitization results in decreased NAc core NMDA receptor function. For A–D, NAc core neurons were voltage clamped at −90 mV and for E–F at +40 mV and evoked EPSCs (0.05 Hz) were recorded for at least 10 min to ensure the stability of baseline recordings. In all experiments, GABAA IPSCs were pharmacologically blocked using bicuculline methiodide (20 μm; Sigma). A, B, Average frequency (A) and amplitude of sEPSCs (B) collected during 6 min epochs at −90 mV from cells in slices from saline (n = 12 cells in 8 mice), nonsensitized (n = 6 cells in 6 mice), and sensitized (n = 8 cells in 8 mice) groups. C, Cumulative probability distributions of sEPSC amplitude obtained in recordings from saline, nonsensitized, and sensitized groups of mice. D, PPR of evoked EPSCs (25, 50, and 250 ms interpulse interval) at −90 mV from saline (n = 15 cells in 9 mice), nonsensitized (n = 12 cells in 9 mice), and sensitized (n = 12 cells in 9 mice) groups. E, Averages of 10 consecutive EPSCs evoked at +40 mV for AMPA/NMDA ratios for saline, nonsensitized, and sensitized groups. Peak AMPA receptor-mediated current was measured at +40 mV (during a 2 ms window, 13 ms after EPSC onset) and NMDA receptor-gated currents were measured in a 10 ms window, 100 ms after EPSC onset. F, AMPA/NMDA ratios in cells recorded from the saline (n = 8 cells in 8 mice), nonsensitized (n = 6 cells in 6 mice), and sensitized (n = 7 cells in 6 mice) groups. IAMPA at +40 mV/INMDA at +40 mv was taken as the AMPA/NMDA ratio. *p < 0.05 for sensitized versus nonsensitized and saline groups.