Figure 1.
SHANK Mutations Causing Autism-Related Phenotypes
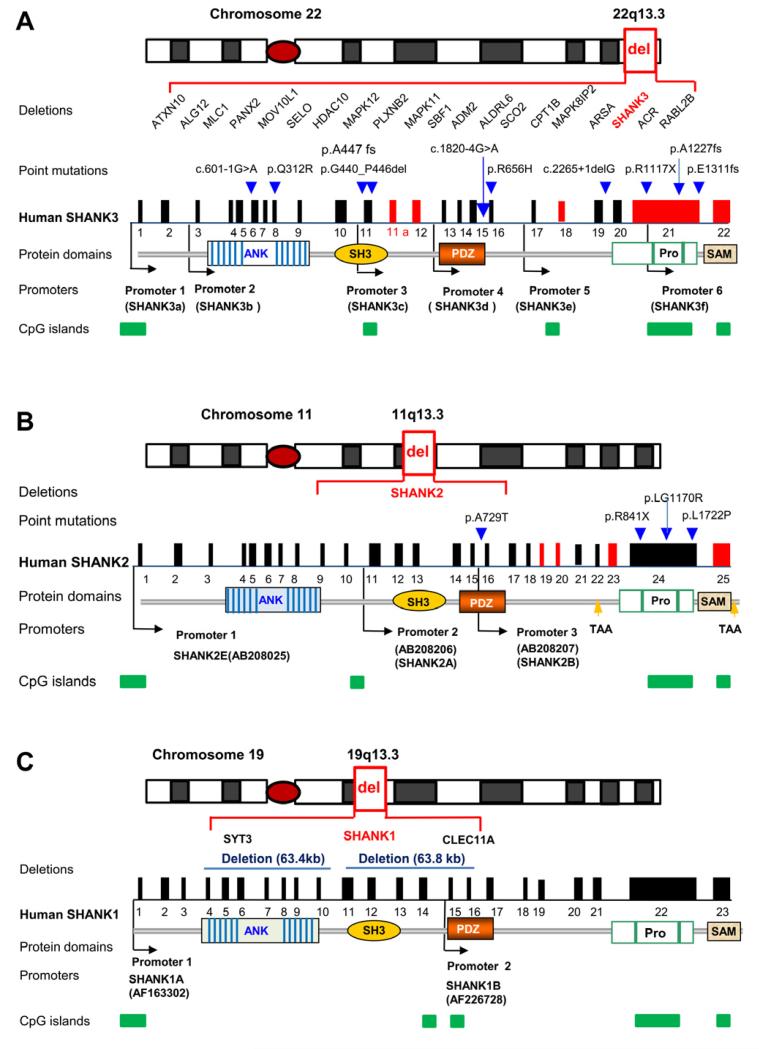
(A) SHANK3 is part of a large gene cluster associated with deletions in chromosome 22q13.3 deletion syndrome, or Phelan-McDermid syndrome, associated with autistic behaviors and intellectual disability (select genes are shown). The deletion sizes vary from 17 kb within SHANK3 to 10 Mb in 22q13.3. SHANK3 gene structure, mutations, and protein domains are shown. Human SHANK3 has 23 exons as deduced from cDNA AB569469 deposited in GenBank. Exon 11a is a newly identified exon. The positions of six identified promoters are indicated as black arrows. The exons in red are alternatively spliced. The positions of point mutations are indicated as blue arrows and the nature of point mutations are as described above the arrow. c.601-1G>A splicing mutation in intron 5 (Hamdan et al., 2011), p.Q312R in exon 8 (Moessner et al., 2007), p.G440_P446del and p.A447fs in exon 11 (Boccuto et al., 2012; Waga et al., 2011), c.1820-4 G>A splicing mutation in intron 15 (Boccuto et al., 2012), p.R656H in exon 16 (Waga et al., 2011), c.2265+1delG splicing mutation in intron 19 (Gauthier et al., 2009), and p.R1117X, p.A1227fs, p.E1311fs in exon 21 (Boccuto et al., 2012; Durand et al., 2007; Gauthier et al., 2010). Protein domains are shown and aligned to corresponding exons (ANK, ankyrin repeat domain; SH3, Src homology 3 domain; PDZ, PSD-95/Discs large/ZO-1 domain; Pro, a proline-rich region containing homer- and cortactin-binding sites; SAM, sterile alpha motif domain). CpG islands are sites of differential methylation and are indicated by green bars.
(B) SHANK2 gene structure, protein domains, isoforms, microdeletions and mutations in ASD. Exons in red are alternatively spliced exons. Microdeletions found in ASD are intragenic and within SHANK2 genomic region. Point mutations found in ASD are indicated as blue arrows and the nature of mutations are described above. Three identifiable promoters corresponding to SHANK2E, 2A, 2B are indicated as black arrow. Two alternative stop codons (TAA) are indicated as yellow arrows.
(C) SHANK1 gene structure, protein domains, isoforms, and microdeletions in ASD. Two small deletions including SHANK1 and two other genes are shown. No pathological point mutations in SHANK1 have been reported in ASD. The positions for two promoters are shown (Lim et al., 1999). The alternative splicing and isoforms have not been fully characterized. In (A)-(C), genomic distance and exons are not drawn to scale.