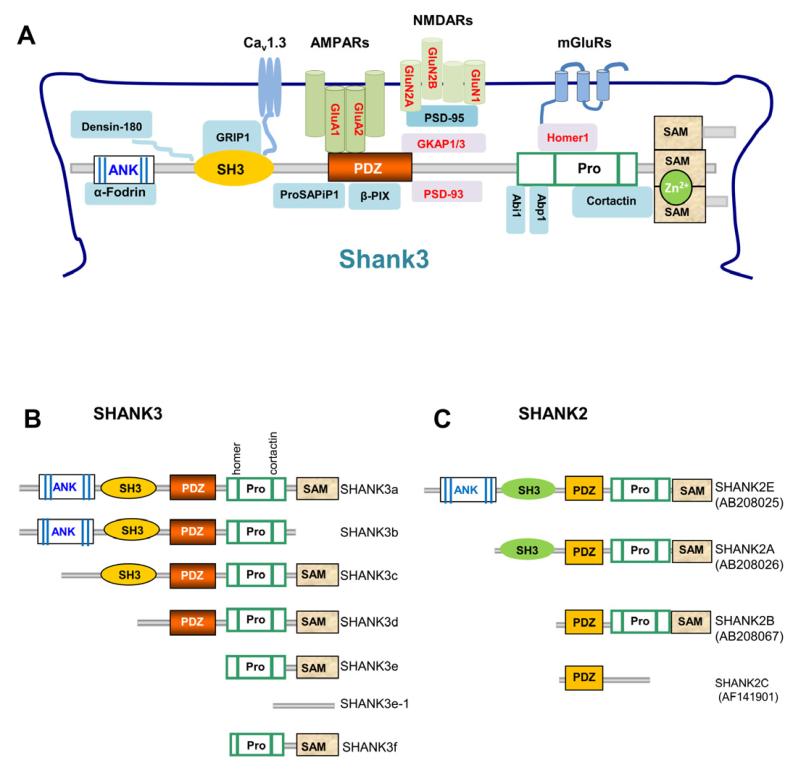
Figure 2.
Shank Protein Interactions and Isoform-Specific Domain Structure
(A) Schematic of the partial Shank protein interactome at the PSD with Shank3 as a model. A more complete list of Shank family interacting proteins is shown in Table 2. Protein domains in Shank family members are similar. Many interacting proteins interact with all three Shank family proteins (Shank1, Shank2, and Shank3) in in vitro assays. The proteins in red font are altered in Shank3 mutant mice.
(B) Diagram of SHANK3 protein isoforms SHANK3a-f. Protein domain structure was deduced from confirmed mRNAs expressed from different promoters in human and mouse brains. Polypeptides have not been validated due to the lack of isoform-specific antibodies. Pro, proline rich region.
(C) Diagram of SHANK2 protein isoforms of SHANK2A, 2B, 2C, and 2E [modified from (Leblond et al., 2012)]. SHANK2C has an alternative stop codon due to the alternative splicing of exons 19 and 20 as shown in Figure 1B.