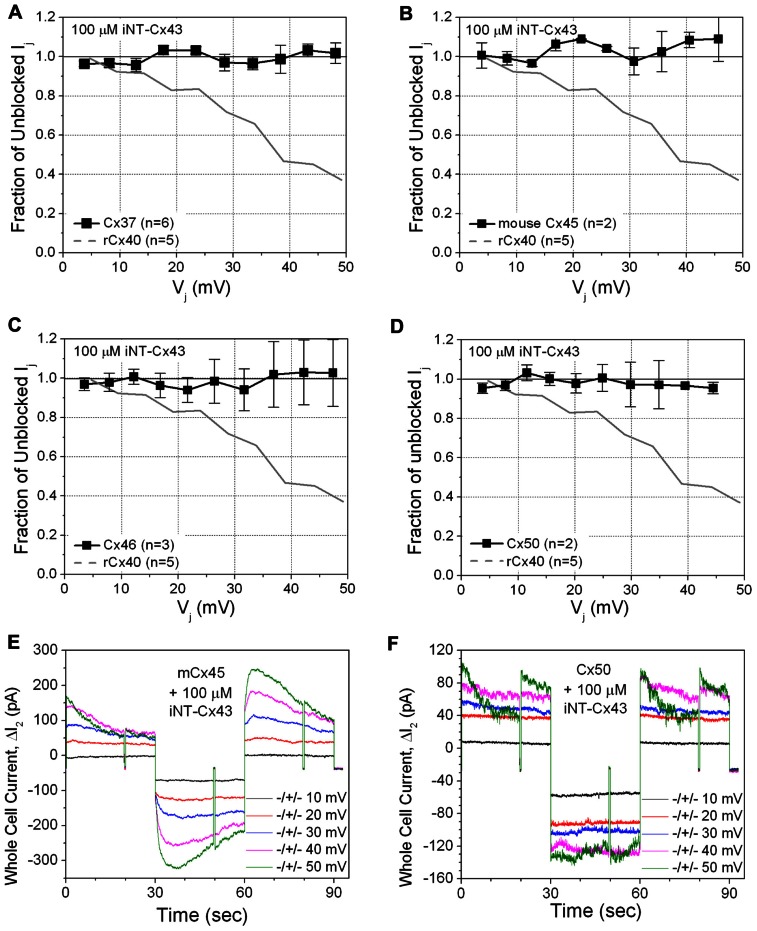
FIGURE 3.
The ability of the iNT-Cx43 peptide to inhibit Cx37 (A), Cx45 (B), Cx46 (C), and Cx50 (D) gap junctions was tested using the same Vj-dependent block protocol as in Figure 2. As a reference, the blockade of rCx40 Ij (continuous gray line) is illustrated in each panel. Unlike rCx40, none of these four connexin gap junctions were significantly inhibited by 100 μM iNT-Cx43 peptide. Actual ΔI2 current traces from Cx45 (E) and Cx50 (F) cell pair iNT-Cx43 peptide experiments illustrating the lack of Ij current block during the +ΔV1 (≅Vj) step, in contrast to the Cx40 experiments shown in Figure 2. Cx45 and Cx50 gap junctions are more Vj-dependent than Cx40 (half inactivation Vj = V0 or V½ ≅ ±30, ±40, or ±49 mV, respectively; Lin et al., 2006; Gonzalez et al., 2007). mCx45 gap junctions prominently display contingent hemichannel gating upon Vj polarity reversal, proposed by Harris et al. (1981), owing to the increased Vj-dependence and lack of fast Vj-gating kinetics of these gap junctions.