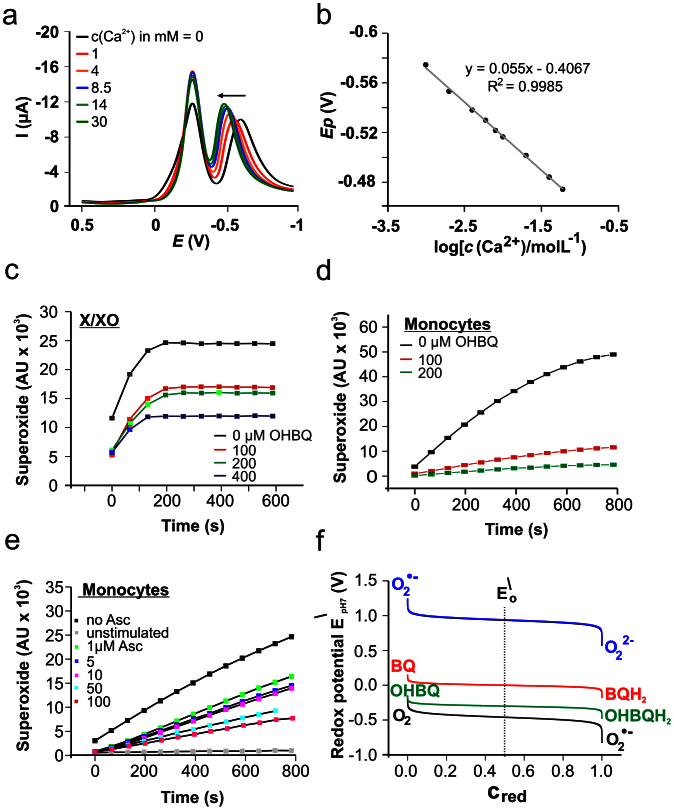
Figure 5. Ca2+-binding and antioxidant properties of OHBQ derivatives.
a) Ca2+ sensitivity of the net SW voltammograms of the reaction mixture at pH 7.4, after incubation of 10 μM BQ in NaOH. SW frequency f = 8 Hz, amplitude Esw = 50 mV, and potential step dE = 1 mV. b) Net SWV peak potential dependence on logarithm of Ca2+ concentration for the response of OHBQ. Evaluation of the antioxidative properties of OHBQ by ESR spin monitoring using the cyclic hydroxylamine CMH and superoxide (•O2–) generated by c) xanthine/xanthine oxidase (500 μM/0.05 U/mL) and d) PMA (1 μM) activated primary human monocytes (5 × 105 cells). e) Ascorbic acid as scavenger for monocyte-produced •O2– instead of OHBQ (2.5 × 105 cells). f) Comparison of the standard redox potentials at pH 7 of the couples BQ/BQH2, OHBQ/OHBQH2 with the oxygen redox potentials, calculated as a function of normalized reduced fraction Cred.